What is a Keylogger? If you’ve ever typed a password, sent a private message, or entered your banking details, imagine someone silently recording every keystroke. That’s the invisible danger keyloggers present. In the fast-evolving world of cybersecurity, keyloggers highlight how attackers can bypass traditional security by targeting human activity rather than breaking complex systems.
Understanding what is a keylogger is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. These tools can be used both for legitimate monitoring and malicious intent. While parents or employers may rely on them for supervision, cybercriminals weaponize them to commit fraud, steal data, and cause harm. In a time when cyber threats, hacking, and even deepfakes dominate the headlines, knowing how keyloggers operate is your first defense against unseen intrusions.
What Is a Keylogger?
What Is a Keylogger refers to software or hardware designed to track and record keystrokes on a device. Every character typed—passwords, emails, or financial data—can be logged and retrieved. Keyloggers are also known as keystroke loggers, monitoring tools, or data-capturing malware.
Although some use keyloggers for parental control or workplace oversight, most discussions around them revolve around malicious intent. They are often hidden inside downloads, fake Windows Update prompts, or phishing emails. Once active, they operate silently in the background, making them difficult to detect.
Breaking Down What Is A Keylogger

To understand what is a keylogger, think of it as an invisible spy quietly recording everything you type—passwords, messages, or financial details.
They come in two main forms:
- Software keyloggers: Hidden in fake downloads or phishing emails, sending logs to attackers.
- Hardware keyloggers: Small devices placed between a keyboard and computer, often unnoticed.
A harmless-looking USB or a fake “system update” can conceal one, silently stealing data for weeks. Because they’re so stealthy, even antivirus tools may miss them. That’s why experts emphasize awareness and good security habits—no software, not even a VPN, can stop a keylogger already on your system.
History of Keylogger
The history of what is a keylogger dates back to the earliest computing days when security researchers experimented with monitoring tools. Over time, these tools were misused for surveillance and crime.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1970s | Early military and research monitoring tools emerge |
| 1990s | First widespread malicious software keyloggers appear |
| 2000s | Hardware keyloggers grow common in workplace attacks |
| 2010s | Advanced malware bundles include keyloggers |
| 2020s | AI-enhanced keyloggers target mobile and IoT devices |
Types of Keylogger
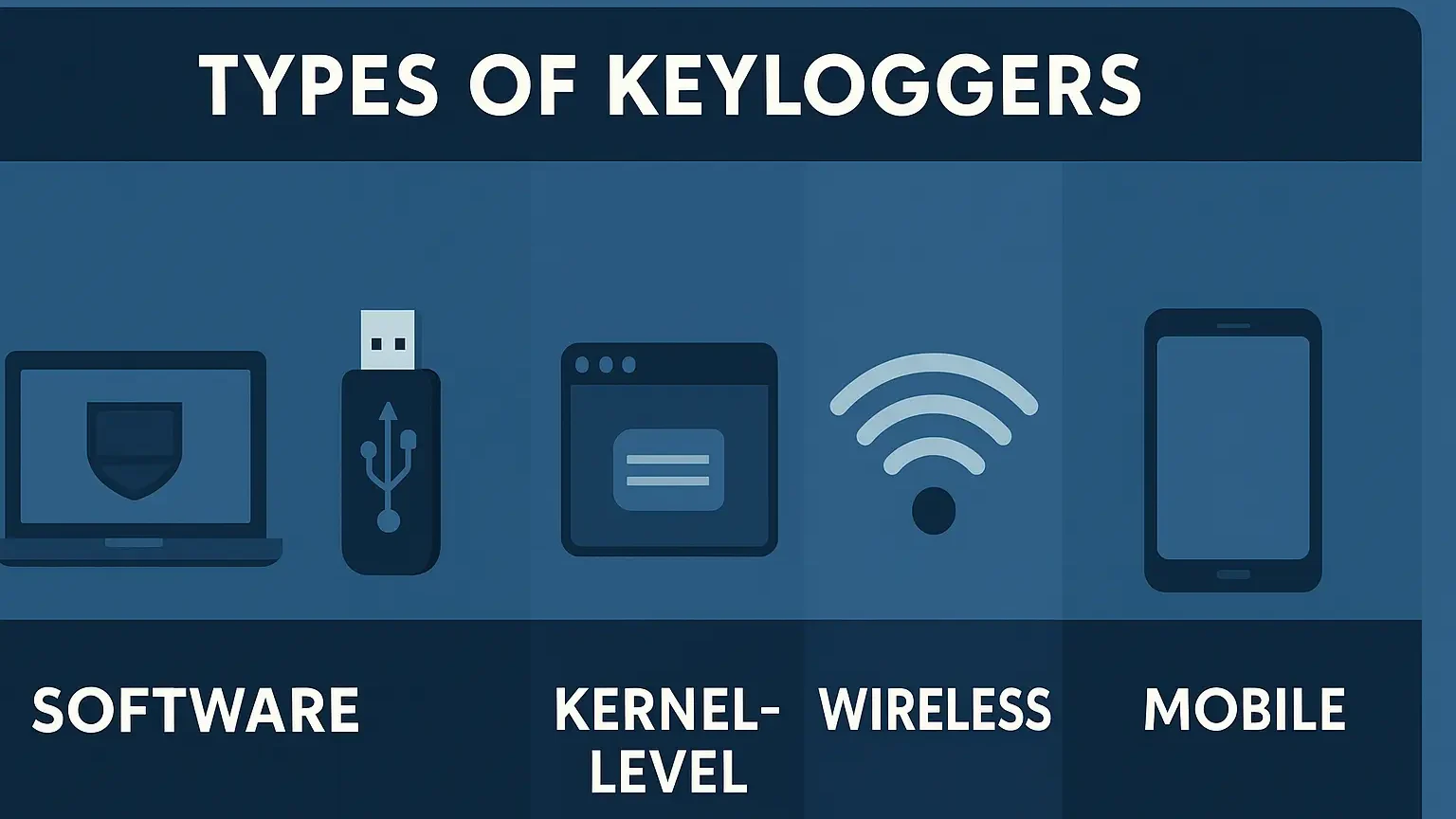
Keyloggers come in different forms, but they all share the same goal—secretly recording keystrokes. Understanding these variations helps spot red flags and prevent compromise.
Software Keyloggers – The most common type, installed through malicious downloads or phishing emails. They run in the background, record keystrokes, and send logs to attackers.
Hardware Keyloggers – Small devices placed between a keyboard and computer, or hidden inside keyboards. They require physical access and are often missed by antivirus tools.
Kernel-Level Keyloggers – Operate deep in the system at the root level, making them very hard to detect. Often used in advanced attacks against governments or financial institutions.
Wireless Keyloggers – Intercept signals between wireless keyboards and receivers, allowing nearby attackers to capture keystrokes.
Mobile Keyloggers – Malicious apps disguised as legitimate software that log texts, social media details, and even crypto wallet credentials.
| Type | Description | Example of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Software | Installed malware capturing keystrokes | Fake downloads or phishing emails |
| Hardware | Physical device between keyboard and PC | Office espionage |
| Kernel-Level | Deep system integration | Attacks on governments/finance |
| Wireless | Captures wireless keyboard signals | Local interception |
| Mobile | Apps logging texts and credentials | Crypto wallet theft |
This breakdown of types of what is a keylogger shows that no device is immune—desktops, laptops, and even smartphones can be compromised.
How Does a Keylogger Work?
A keylogger works by silently embedding itself into a device and recording everything a user types. It usually begins with infection—through phishing emails, fake software updates, malicious downloads, or even hardware devices attached to keyboards. Once active, it runs unnoticed in the background, capturing sensitive information such as passwords, banking details, or private messages. The collected data is then either stored locally or secretly transmitted to a remote server controlled by the attacker. Finally, cybercriminals exploit this stolen information for fraud, identity theft, or espionage, making keyloggers one of the most dangerous and deceptive cybersecurity threats.
Uses of a Keylogger
The uses of what is a keylogger are broad and often troubling. While some applications are legitimate, many are malicious. Recognizing these uses provides clarity about why keyloggers remain one of the most dangerous tools in cybercrime.
Parental Control
Parents sometimes install keyloggers to monitor children’s online activity. They want to ensure their kids stay safe from predators, scams, or harmful websites. For example, a parent might check for signs of bullying or inappropriate content. In this case, keyloggers serve as protective tools, though they must be used responsibly and with transparency.
Workplace Monitoring
Employers may deploy keyloggers to track productivity or detect insider threats. While controversial, some organizations argue that monitoring prevents data leaks and policy violations. For instance, in industries handling sensitive information like finance, monitoring tools help ensure compliance. However, critics argue this blurs the line between security and employee privacy.
Criminal Exploitation
The most infamous use of what is a keylogger is by cybercriminals. They use it to steal banking credentials, personal data, or trade secrets. Picture a victim typing login details to an online broker. A keylogger instantly captures the data, allowing criminals to access accounts and launch fraud schemes. These schemes often include shady investment opportunities promoted through stolen email lists.
Financial Fraud and Crypto Theft
Keyloggers are frequently tied to financial theft. Criminals monitor users active in the crypto market or exploring the coin market, stealing wallet keys and login details. A single slip—typing your blockchain wallet password into a compromised device—could mean losing thousands in cryptocurrency. This highlights why securing digital assets is so important.
Espionage and Surveillance
Governments and intelligence agencies have used keyloggers in espionage. While often justified as national security, it sparks debates about privacy rights. Attackers in corporate espionage also use them to steal blueprints, strategies, or sensitive client data. Imagine a rival company planting spyware in a competitor’s office to gain unfair advantage.
Everyday Harassment
Not all uses of what is a keylogger involve major crimes. In personal disputes, some use them to monitor partners or friends, showing how invasive they can be. From parental safety to fraud, keyloggers affect daily life. Even with tools like Express VPN, users remain at risk if spyware slips in. Awareness and prevention remain the best defenses.
Conclusion
Keyloggers may seem invisible, but their impact is significant. From parental monitoring to corporate oversight and outright cybercrime, they blur the line between legitimate use and malicious intent. Their stealth makes them especially dangerous, silently gathering sensitive information like passwords, financial details, or business data. Whether it’s stolen accounts, drained crypto wallets, or corporate espionage, the risks highlight why awareness and vigilance are essential. By understanding how keyloggers work and where they hide, individuals and organizations can take smarter steps to protect their data—because in cybersecurity, prevention is the difference between safety and exposure.
Resources
- Kaspersky – What is a Keylogger?
- Norton – Keylogger Malware Explained
- McAfee – Learn About Keyloggers
- CISA – Keylogger Information
- Trend Micro – What is a Keylogger?
