Casino site database management is the backend system that controls how player data is stored, organized, synchronized, and retrieved across an online casino platform to maintain accuracy, consistency, availability, and traceable records.
Key Takeaways
- Casino site databases are distributed systems, not single storage units.
- Player data is segmented by function to support performance and reliability.
- Databases record states and historical records, not game logic or outcomes.
- Strong database design is essential for accuracy, continuity, and operational trust.
Definition
Casino site database management refers to the technical processes and systems used to store, maintain, query, and control access to player-related data within an online casino platform.
What it means
In an online casino environment, the casino site database acts as the authoritative record for all player-related information. This includes identity details, account status, balances, session activity, gameplay history, transaction records, and system logs required for monitoring and audits.
Casino platforms typically rely on a multi-database architecture. Relational databases are commonly used for structured data such as player profiles, account balances, and transaction histories. These systems enforce strict consistency rules so that related records remain synchronized, even when large numbers of actions occur at the same time.
Alongside relational systems, non-relational databases are often used to manage high-volume or rapidly changing data. Examples include active session tracking, temporary gameplay states, and event logging. These databases are optimized for fast write operations and horizontal scalability rather than complex relational queries.
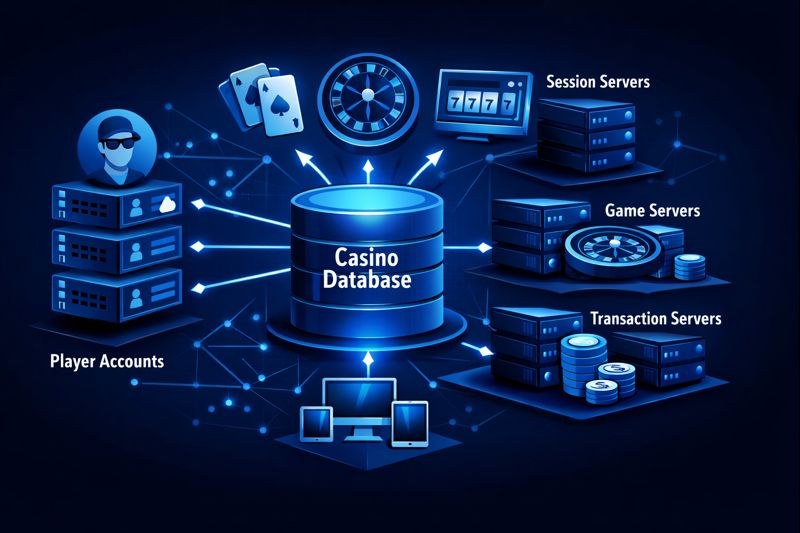
When a player interacts with a casino site, backend services act as intermediaries between the user interface and the database layer. A login request triggers authentication checks and retrieves account status from a relational database. At the same time, a session record is created or updated in a separate data store designed for real-time access.
Each meaningful action generates database operations. Entering a game, completing a round, updating account information, or logging out results in records being written or updated. These records include timestamps, identifiers, and status markers so activity can be reconstructed later if required. This structure supports internal monitoring, dispute handling, and regulatory review.
To maintain performance, casino site databases use indexing strategies to speed up frequent queries, such as retrieving recent transactions or account details. Caching layers may temporarily store commonly accessed data to reduce load on primary databases while preserving a single source of truth.
Replication is a core element of casino site database management. Databases also support operational oversight. Historical records of player activity, system events, and transactions must be retrievable for audits, compliance reviews, and internal analysis, and that expectation applies on real platforms like our casino where traceability is part of daily operations.
Why it matters
Casino platforms operate continuously and process large volumes of concurrent activity. Player balances, session states, and recorded outcomes must remain consistent across systems at all times. Even small inconsistencies can surface as visible errors, such as incorrect balances or interrupted sessions.
Databases also support operational oversight. Historical records of player activity, system events, and transactions must be retrievable for audits, compliance reviews, and internal analysis. These requirements influence how data is structured, how long it is retained, and how access is logged and controlled.
Scalability is another critical factor. As user numbers grow, databases must handle increasing read and write demands without introducing latency. Well-designed casino site database systems allow platforms to scale by adding resources rather than relying on a single overloaded component.
The Casino Site Database management also contributes to fault tolerance. By separating data by function and maintaining redundant systems, platforms reduce the impact of individual failures. This design prioritizes data integrity and service continuity over architectural simplicity.
Mini-Checklist
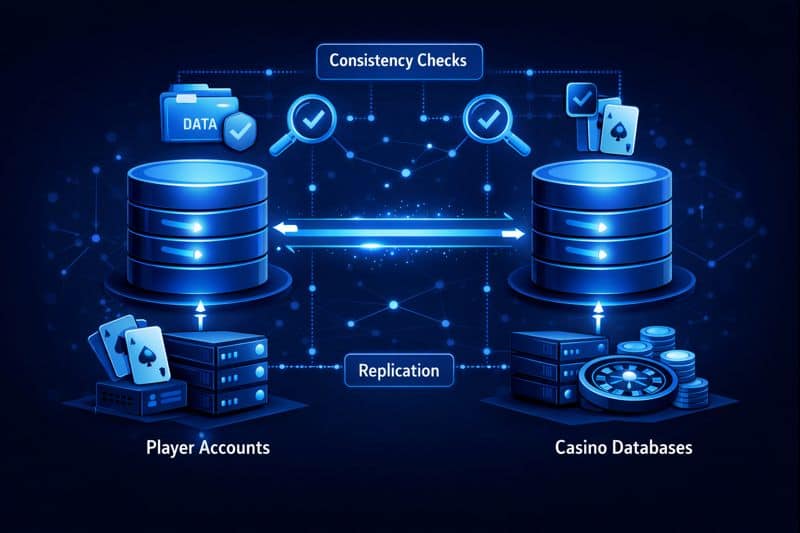
- Player data is segmented by function, not stored in one system
- Real-time activity uses databases optimized for frequent updates
- Account and transaction records prioritize consistency and traceability
- Replication and backups are part of standard operations
Common mistakes
A common misconception is that all player data is stored in one centralized casino site database. In practice, data is distributed across multiple systems to improve performance, scalability, and resilience.
Another misunderstanding is that databases determine game outcomes. Databases store inputs and results, but game logic and randomization are handled by separate software components.
It is also incorrect to assume that casino site database management is only about security. While access control is important, database management also includes data modeling, performance tuning, replication planning, and long-term storage strategies.
Some assume that faster databases are always better. In casino environments, accuracy and consistency often take priority over speed. Systems are designed to confirm that data is written correctly before it is displayed or acted upon.
Examples
When a player logs into a casino site, the platform retrieves account credentials and status from a relational database. At the same time, a session record is created in a separate data store that tracks active users. This separation ensures that session updates do not interfere with account integrity.
During gameplay, each significant action generates an event that is written to a database optimized for high-frequency updates. Once a game round concludes, the final outcome is stored in a transaction table linked to the player’s account. This record supports later reporting, auditing, or dispute resolution.

Another common example involves player account updates outside of gameplay. When a user changes account information, such as contact details or security settings, the update is written to a core account database that enforces validation rules and version control. The system records both the previous and updated values with timestamps to maintain an audit trail, ensuring changes are traceable without affecting live session or gameplay data.
For reporting and analysis, casino platforms often rely on read-only replicas or dedicated analytical databases. These systems allow administrators to generate summaries and operational insights without impacting live gameplay performance.
FAQ
Do casino sites use only one type of database?
Most platforms use a combination of relational and non-relational databases, each selected for specific workloads.
Is player data stored permanently?
Some data is retained long term for compliance and auditing, while other data such as session states may be temporary.
Does the database handle payments directly?
Payment processing is handled by separate financial systems, but databases store transaction records and status updates.
Resources
- SoftwareReviews. Casino Management Software
- GammaStack. The Ultimate Guide to Casino Management System
- SDLC Corp. Choosing the Right Database for Casino Game Scaling
- Limeup. Casino Software Providers: Platforms and Backend Systems
- Tecpinion. The Most Powerful Casino Management System Companies Shaping the Future of Gambling
