Consider a scenario where your organization is compromised not by a direct cyberattack but through a familiar employee’s unsecured laptop. Despite firewalls and a traditional security perimeter, sensitive information is quickly accessed and extracted. In this case, trust within the network became the weakest link. This is where Zero Trust Security becomes essential.
As more companies transition to cloud environments and hybrid workplaces, traditional security measures fall short. Zero Trust Security provides a forward-looking approach that protects data, systems, and users through continuous validation and limited access.
What Is Zero Trust Security?

Zero Trust Security is a strategic cybersecurity approach that assumes no entity should be trusted automatically. Every access request, whether it comes from inside or outside the network, must be verified before being granted. This means that users, devices, and applications must all prove they are legitimate and safe to interact with sensitive resources.
Rather than being a single product, Zero Trust is a security philosophy that integrates with many tools and processes. The goal is to protect information by ensuring strict access control, continuous monitoring, and real-time decision-making.
How Does Zero Trust Security Work?
Zero Trust Security works by eliminating assumptions about trust within the network. It follows a structured process:
- User Authentication: The system confirms the user’s identity using secure methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication.
- Device Compliance Checks: Devices must meet certain requirements, including security patches and software updates, before gaining access.
- Real-Time Risk Assessment: The system evaluates contextual signals such as location, device type, and behavior to determine whether to allow access.
- Policy Enforcement Engines: Access decisions are made based on a dynamic set of rules. If the conditions are met, access is approved.
- Continuous Monitoring: All activities are tracked and logged to detect anomalies or threats quickly.
Principles of Zero Trust Security
Verify Explicitly
Zero Trust Security begins with the need to verify every access request. This means checking user identity, device health, and other contextual factors before access is granted. The system performs these checks continuously throughout the user session. By doing so, it ensures that access is always based on reliable data.
Use Least Privilege Access
This principle limits each user’s access to only what they need to perform their responsibilities. It reduces unnecessary exposure to sensitive information and lowers the risk of internal misuse. Organizations regularly review access rights and adjust them when necessary. This approach helps maintain a secure and organized environment.
Assume Breach
Under this principle, systems operate with the understanding that a security breach could already be occurring. Every action is monitored, and each interaction is evaluated with caution. This proactive mindset enables early detection and containment of threats. It ensures the organization can respond quickly and effectively when incidents arise.
History of Zero Trust
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2004 | Jericho Forum challenges perimeter-based security models. |
| 2010 | Forrester introduces the term “Zero Trust Security”. |
| 2014 | Google launches BeyondCorp, a Zero Trust initiative. |
| 2020 | NIST releases official Zero Trust Architecture guidelines. |
| 2021 | The U.S. government mandates Zero Trust for all federal agencies. |
Zero Trust has steadily evolved from a theoretical concept into a practical and widely adopted security strategy.
Types of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA grants access to individual applications, not the whole network. It authenticates users and devices before connecting them to specific resources. This reduces exposure and prevents lateral movement. ZTNA is a safer alternative to traditional VPNs.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM verifies each user’s identity before granting access. It uses multi-factor authentication, role-based access, and identity governance. These tools ensure users only access what they need. IAM is the foundation of secure authentication in Zero Trust.
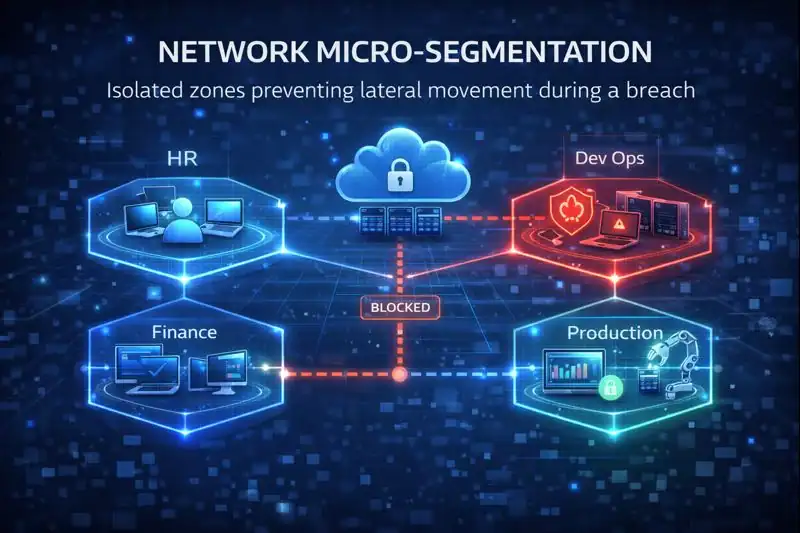
Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation breaks the network into smaller, isolated zones. It enforces strict access controls between each zone. If attackers breach one zone, they cannot move to others. This minimizes damage during a security incident.
| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ZTNA | Controls application access based on identity. | Cloud-based VPN replacement. |
| IAM | Manages user identities and permissions. | Multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Micro-Segmentation | Divides networks into isolated zones. | Limiting lateral movement in a breach. |
How Zero Trust Security Works
A typical Zero Trust workflow involves several steps designed to protect access from every angle:
- User Authentication: Identity is verified using multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Device Compliance: The system checks for updated software, patches, and threat scans.
- Granular Access: Access is provided only to specific resources based on role or function.
- Continuous Monitoring: All sessions are logged, and behavior is analyzed to detect anomalies.
This cycle repeats for every interaction, creating a dynamic and secure environment.
Pros & Cons
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Strengthens protection against insider threats | Implementation can be complex and resource-intensive |
| Enables secure remote and hybrid work | Requires continuous monitoring and updates |
| Reduces the impact of breaches | Needs staff training and change management |
| Enhances regulatory compliance | May involve new tool adoption |
Despite the challenges, the benefits of Zero Trust far outweigh the initial efforts required for implementation.
Applications of Zero Trust Security
Enterprise IT
Large corporations use Zero Trust to secure access for globally distributed teams. Google’s BeyondCorp initiative is a clear example of this approach in action. It eliminates the need for VPNs and ensures that employees access only what is necessary. This helps maintain both productivity and security.
Healthcare
Hospitals and clinics apply Zero Trust to protect patient health records and comply with privacy laws. With solutions like Prisma Access, only authorized personnel can reach sensitive systems. This ensures data security whether users are onsite or remote. Healthcare organizations also benefit from better control during audits.
Finance
Banks and financial institutions use Zero Trust to secure transactions and protect customer data. Platforms like IBM Security Verify detect abnormal behavior and apply real-time safeguards. This helps prevent fraud and ensures regulatory compliance. Customers benefit from safer online experiences.
Education
Schools and universities implement Zero Trust to secure digital classrooms and learning platforms. Students, teachers, and staff can access tools from various devices while staying protected. This model keeps educational data safe from threats. It also supports flexible learning without compromising security.
Government
Government agencies use Zero Trust to protect national security systems. It supports compliance with strict regulations such as FISMA and CMMC. By segmenting networks and enforcing identity checks, these institutions can better resist cyberattacks. The model ensures accountability across departments.
E-Commerce
Retailers adopt Zero Trust to protect customer data and payment processes. It helps detect unauthorized access, prevent session hijacking, and limit exposure to financial data. Customers experience safer transactions. Meanwhile, businesses remain compliant with data protection laws.
