If you have dipped your toes into crypto, you may have wondered: What is Uniswap? At its simplest, it is one of the most influential decentralized exchanges (DEXs) in the world of blockchain. Instead of relying on a bank or a centralized exchange, it allows people to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other using smart contracts.
This makes it a cornerstone of decentralized finance (DeFi). Millions of users now depend on it for fast, permissionless trading. Understanding what is uniswap is more than curiosity—it’s essential for anyone looking to explore crypto beyond just holding coins.
What is Uniswap?
It is a decentralized exchange built on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows users to swap tokens without intermediaries, using automated liquidity pools instead of traditional order books. Also called a DEX, it enables peer-to-peer trading and supports thousands of ERC-20 tokens.
Breaking Down Uniswap
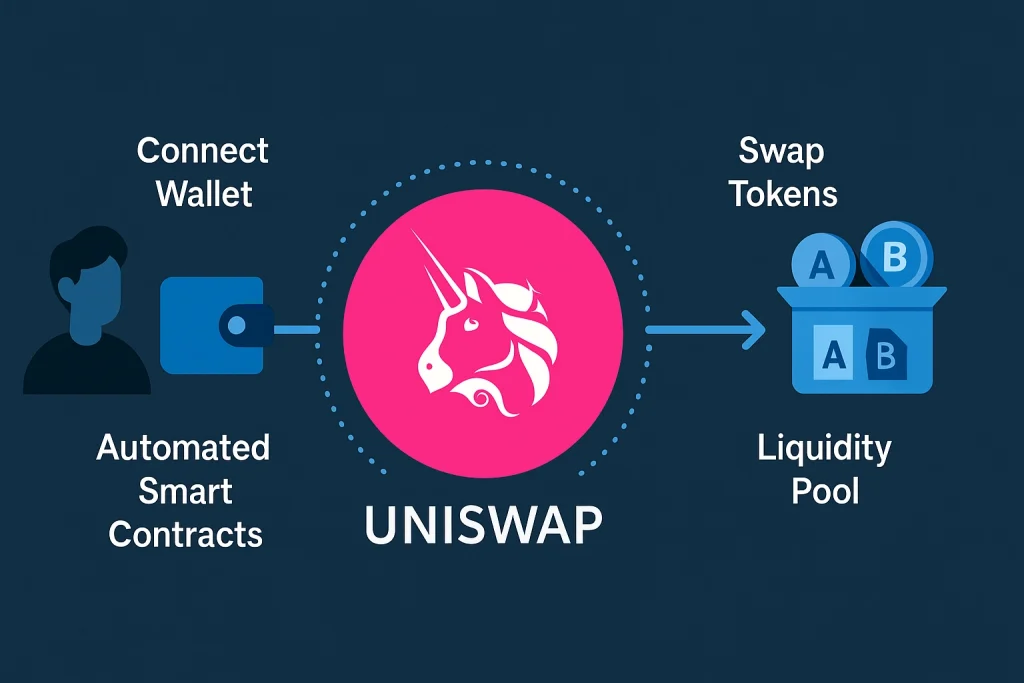
To really understand what is Uniswap, think of it as a decentralized alternative to traditional exchanges like Coinbase or Binance. Instead of middlemen, it uses smart contracts on Ethereum to let users trade directly.
At its core, what is Uniswap built on the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. Traders swap tokens with liquidity pools instead of waiting for a match, and prices adjust automatically through a formula. Liquidity providers earn fees in return, making it attractive for both sides.
Another key part of what is Uniswap is that it’s non-custodial—you control your private keys, reducing risks like hacks or frozen withdrawals. It’s also highly accessible, with no KYC requirements, though this openness can attract scams and fake tokens.
Finally, what is Uniswap has evolved through multiple versions (V1 to V4), each improving efficiency, fees, and features. In short, it’s not just an exchange—it’s a gateway into the broader world of DeFi.
History of Uniswap
It was launched in 2018 by Hayden Adams, inspired by Ethereum’s creator, Vitalik Buterin. The goal was simple: make token swapping easy and decentralized.
Since then, it has grown into one of the largest decentralized exchanges by volume. It became a central player during the DeFi boom of 2020, with billions in daily trading volume. Its native governance token, UNI, was introduced in September 2020, giving users a voice in platform upgrades.
| Year | Development Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2018 | Launch of Uniswap V1 |
| 2020 | Release of V2 with new features |
| 2020 | UNI token airdrop introduced governance |
| 2021 | Uniswap V3 launched with concentrated liquidity |
| 2022+ | Expansion across multiple blockchains |
Types of Uniswap
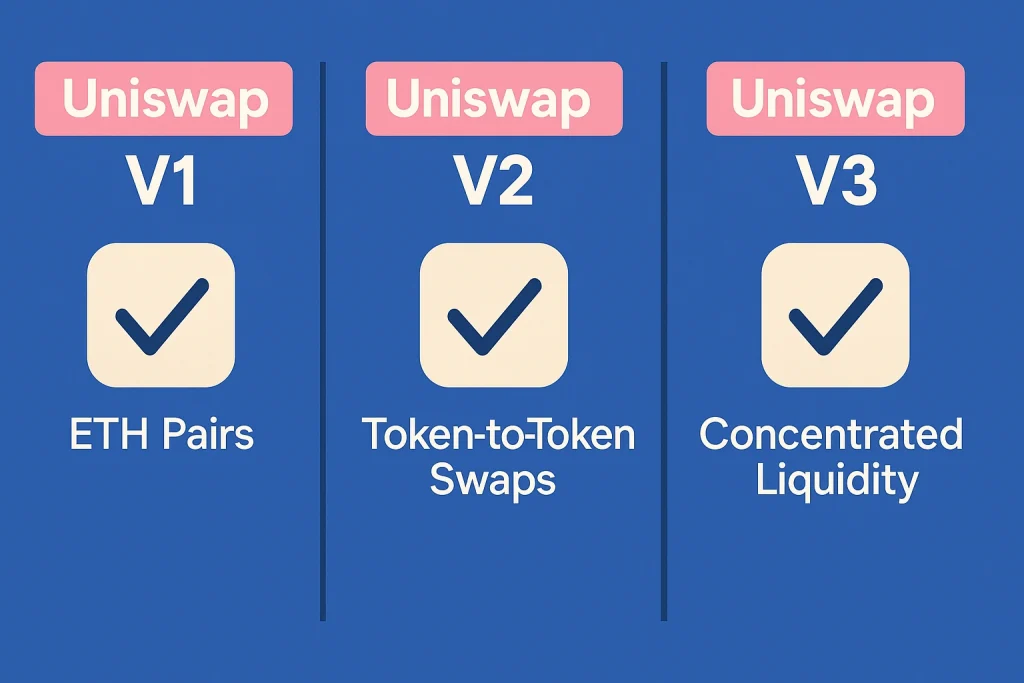
Over the years, different versions of Uniswap have been developed to improve user experience.
Uniswap V1
Launched in 2018, V1 introduced the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model to the world. It allowed users to swap ERC-20 tokens, but every trade had to be paired with ETH. For example, if you wanted to swap DAI for USDC, you’d first swap DAI → ETH, then ETH → USDC. This worked but was inefficient and costly.-
Uniswap V2
In 2020, V2 brought major improvements. It allowed direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps, eliminating the need to route through ETH. It also introduced price oracles, making it possible for developers to use Uniswap data for DeFi apps. Another big upgrade was flash swaps, where users could withdraw tokens instantly as long as they repaid them within the same transaction—paving the way for arbitrage strategies.
Uniswap V3
Released in 2021, V3 focused on efficiency and flexibility. It introduced concentrated liquidity, letting liquidity providers (LPs) choose custom price ranges for their funds. This meant LPs could deploy capital more strategically and earn higher returns instead of spreading liquidity across the entire market. V3 also added multiple fee tiers, catering to different risk levels. However, it made providing liquidity more complex, often requiring active management.
Uniswap V4 (Upcoming / In Development)
Uniswap Labs announced V4 in 2023. It aims to reduce costs by introducing “hooks”, which let developers customize pools with unique features such as on-chain limit orders, dynamic fees, or auto-compounding rewards. It will also use singleton contracts, reducing gas fees significantly by handling multiple pools in a single smart contract.
| Version | Key Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| V1 | ETH-paired swaps, first AMM model | Inefficient, all trades routed through ETH |
| V2 | Direct ERC-20 swaps, price oracles, flash swaps | Still relatively high gas fees |
| V3 | Concentrated liquidity, multiple fee tiers, higher efficiency | Complex for liquidity providers |
| V4 | Hooks for customization, singleton contracts for lower gas | Still under development |
How does it work?
It works through smart contracts on Ethereum. Users connect their wallets, choose tokens to swap, and approve transactions. The AMM handles pricing automatically, while liquidity providers supply the funds in pools. All trades happen directly on-chain, giving users transparency and control.
Pros & Cons
Before diving in, it helps to see both sides of what is Uniswap—its strengths and its challenges.
Pros
Permissionless and open to everyone
Anyone with a crypto wallet can access Uniswap without needing approval, lengthy sign-ups, or KYC. This openness is a big part of what is Uniswap and why it’s considered revolutionary in DeFi.
Non-custodial, users keep control
Unlike centralized exchanges that hold your funds, Uniswap lets you stay in full control of your private keys. Understanding what is Uniswap means knowing that your assets are never locked by a third party.
Provides passive income via liquidity
Users can supply tokens to liquidity pools and earn a share of the trading fees. This makes what is Uniswap attractive not only for traders but also for investors seeking passive income.
Transparent and decentralized
All trades happen on-chain through smart contracts, ensuring full transparency. This decentralization is central to what is Uniswap, making it a trusted protocol in the crypto community.
Cons
High gas fees on Ethereum
Transactions can be costly during times of network congestion, making small trades less practical.
Risk of fake tokens
Since anyone can list a token, scams and imitations are common, requiring extra caution from traders.
Complex for beginners
New users may find liquidity pools, AMMs, and impermanent loss confusing, creating a learning curve.
Exposure to impermanent loss
Liquidity providers face the risk of losing value compared to simply holding tokens, especially during volatile markets.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Permissionless and open to everyone | High gas fees on Ethereum |
| Non-custodial, users keep control | Risk of fake tokens |
| Provides passive income via liquidity | Complex for beginners |
| Transparent and decentralized | Exposure to impermanent loss |
Uses of Uniswap
It is not just for swapping tokens—it has many real-world uses in crypto.
Token Swaps
The most common use of Uniswap is exchanging one ERC-20 token for another. Traders often use it to access new tokens before they appear on centralized exchanges.
Liquidity Provision
Investors can add their assets to liquidity pools and earn a share of trading fees. This turns idle tokens into income-generating assets.
Yield Farming
During the DeFi boom, many platforms integrated with Uniswap pools, allowing users to stake liquidity provider (LP) tokens for additional rewards.
Conclusion
Uniswap has grown from a simple token swap experiment into one of the most powerful platforms in decentralized finance, with each version—V1, V2, V3, and the upcoming V4—introducing features that make trading faster, smarter, and more efficient. It offers traders open access to thousands of tokens without middlemen, gives liquidity providers opportunities to earn passive income, and provides developers with a foundation for building innovative financial tools. However, with this freedom come risks such as fake tokens, scams, and impermanent loss, which users must navigate carefully. Ultimately, Uniswap is more than just an exchange—it is a gateway into the decentralized economy, and by understanding its history, features, and risks, users can approach it with confidence and caution.
Resources
- Uniswap – Official Website
- Coinbase – What is Uniswap?
- Uniswap Docs – Beginner’s Guide to Uniswap
- Kraken – Uniswap Explained
- Investopedia – Uniswap Definition
