Have you ever wondered how your GPS maps out the shortest route, or how the internet connects billions of people worldwide? Beneath all these marvels lies an elegant, often invisible framework called topology. In the realm of technological trends, understanding this technology opens doors to groundbreaking innovations and helps demystify the systems we use every day.
Let me take you back to a moment when I was completely lost in a foreign city, relying solely on my phone to get around. Despite spotty signals, the navigation app recalculated and rerouted me in seconds. I was amazed. Later, I learned this magic wasn’t just clever programming; it was the network architecture at play. This realization sparked a fascination that brought me to today—sharing this dynamic, powerful idea with you.
What is Topology?
At its core, it is the mathematical study of shapes, spaces, and how they transform. But don’t let the math scare you off! In technological contexts, this network architecture is more about how elements are arranged and connected rather than what they look like.
Think of it as a blueprint that defines relationships between components, be it in a network, a system, or even in the structure of the universe. Variations of the term include “network topology,” “spatial topology,” or even “geometric topology,” depending on the field of application.
Breaking Down Topology
So, what makes it so special? Let’s break it down.
Imagine a network—say your home Wi-Fi setup. You have devices (like phones and laptops) that connect through a router. How they are linked, the pathways data travels, and the pattern they form—that’s the network’s topology.
It isn’t just about connectivity; it’s also about resilience. For instance, a mesh topology ensures that even if one node fails, others can still communicate. That’s why topology plays a critical role in building reliable systems.
It also shows up in less obvious places. Think of Google Maps rerouting traffic. The streets and intersections form a topological network. It’s not the distance but the connection and flow that matter most.
History of Topology

It’s roots go back to the 18th century, when a Swiss mathematician named Leonhard Euler solved the famous problem of the Seven Bridges of Königsberg. His work laid the foundation for graph theory, which is central to modern architecture.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1736 | Euler introduces the concept through the Seven Bridges problem |
| 19th Century | Formal development of topology in mathematics |
| 20th Century | Applications in physics, data, and technology expand |
| 21st Century | It becomes integral in computer science, AI, and futuristic technology |
Types of Topology
It comes in different flavors, especially in tech. Here are a few key types:
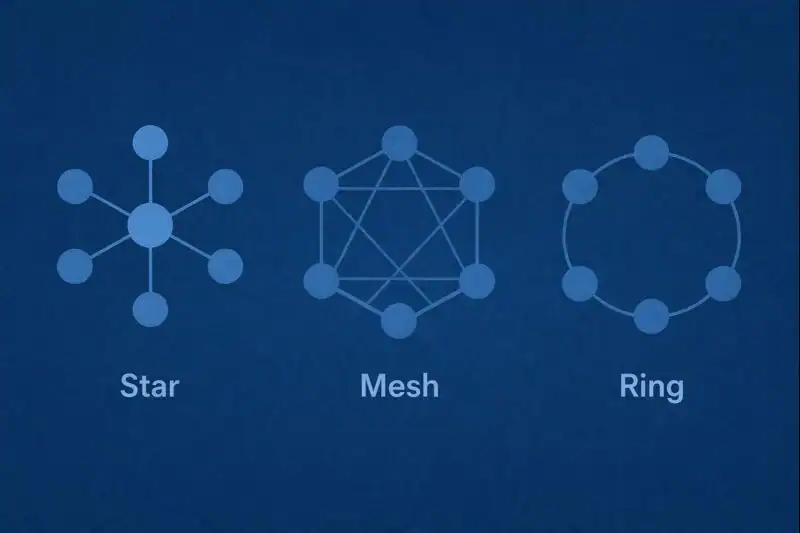
Star Topology
All devices are connected to a central hub. It’s simple and easy to manage.
Example: Your office network likely uses this.
Ring Topology
Each device connects to two others, forming a circular path.
Example: Early local area networks (LANs) often used this setup.
Bus Topology
All devices share a single communication line. It’s cost-effective but prone to traffic issues.
Example: Traditional Ethernet setups.
Mesh Topology
Every device connects to every other. This offers excellent redundancy.
Example: Used in military communications and smart homes.
Tree Topology
A combination of star and bus topologies. It supports scalability.
Example: Enterprise networks with layered access.
How Does Topology Work?
Let’s walk through an example.
Imagine a smart home with multiple IoT devices. Your lightbulbs, thermostat, and speakers are all connected. The arrangement of these devices defines your home’s topology. When you use your phone to dim the lights, the request travels through a route defined by this setup.
It governs how fast the message reaches, how reliable the connection is, and what happens if a device goes offline. A mesh setup might reroute the message through another path, ensuring your lights still dim smoothly.
This logic isn’t limited to homes. Cities, industries, even space networks use similar principles.
Pros & Cons
When designing any complex web of connections within digital systems, understanding the structure of relationships becomes crucial. These configurations form the backbone of reliable, efficient communication networks. Whether it’s how your home gadgets sync or how data flows in a multinational cloud system, the arrangement of these elements can make or break performance.
In this framework of interconnected setups, thoughtful design ensures adaptability and resilience. Yet, with such benefits come challenges—from setup costs to maintenance complexities. Here’s a breakdown:
| Pros | Cons |
| Enhances system reliability | Can be complex to design |
| Improves communication flow | Some setups are costly |
| Adapts to new inventions easily | Maintenance can be challenging |
| Ideal for iot devices | May require specialized hardware |
In short, choosing the right network structure means balancing cost, reliability, and future scalability.
Uses of Topology
When building complex digital ecosystems, the way different parts are organized plays a pivotal role in their success. These configurations are responsible for ensuring efficient communication, scalability, and fault tolerance across various technologies. From smart homes to massive enterprise networks, the way components are structured impacts everything—from speed to reliability. But while such structured systems offer impressive advantages, they’re not without drawbacks. Planning and maintaining them can demand significant investment, time, and expertise. Whether you’re streamlining personal devices or architecting a global network, it’s essential to weigh the strengths and limitations of these intricate connection strategies.
Internet Infrastructure
The internet relies heavily on mesh and star topologies to ensure global connectivity. That’s why a single point of failure rarely crashes the whole system.
Smart Homes
With the rise of iot devices, it defines how gadgets talk to each other. A well-planned setup means your home remains functional even when one component glitches.
Space Exploration
NASA uses topological models to plan satellite networks and planetary communication systems. It’s about ensuring a message from Mars reaches Earth without a hitch.
Advanced Technology Systems
Data centers, cloud platforms, and edge computing all depend on dynamic topologies for optimized performance.
New Inventions in Healthcare
From wearable monitors to robotic surgeries, it governs data routes, ensuring precision and real-time feedback.
Innovation in Transportation
Think of autonomous cars navigating smart cities. Topological models help manage traffic flow and prevent congestion.
Resources
- Internet Archive – Introduction to Topology
- Cisco – What Is Network Topology?
- NASA – NASA’s Communications Networks
- MIT Technology Review – MIT Technology Review
- IEEE – A Study on Topology in Computer Network – IEEE Xplore
