Let’s take a moment to think about how fast the world has become — everything is about speed. We expect web pages to load instantly, files to transfer in seconds, and programs to launch with a single click. And at the heart of all that speed? A powerful storage technology called NVMe. If you’ve ever asked yourself “What is NVMe?”, you’re in for an exciting ride.
In the realm of technological trends, It stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express and is one of the hottest innovations transforming how we interact with data. It’s not just another acronym — it’s the brainchild of engineers who wanted storage to catch up with our need for speed. Whether you’re a gamer, video editor, developer, or just someone who wants a snappy laptop, it is something you need to understand.
What is NVMe?
It stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, and it’s a protocol that allows your computer to read and write data at lightning-fast speeds. It’s specifically designed to communicate with SSDs (Solid-State Drives) over high-speed PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) lanes.
It is not the storage drive itself — it’s how the storage talks to your system. It was built from the ground up to take advantage of flash memory’s capabilities, unlike older protocols like SATA that were originally designed for spinning hard drives.
Breaking Down NVMe
To really get it, picture this: imagine you’re trying to send a package across town. Using older storage protocols like SATA is like mailing it through standard postal service. But why? That’s your same package in a high-speed drone that delivers it straight to the recipient’s door in record time.
Key Components of NVMe:
- PCIe Interface: NVMe leverages PCIe lanes, the same ones used by high-performance graphics cards, allowing data to travel much faster than SATA.
- Parallelism: NVMe can handle thousands of simultaneous queues with thousands of commands per queue — perfect for multitasking.
- Low Latency: Faster response times mean your system can access and process data almost instantly.
- Scalability: NVMe is built with future growth in mind, from high-end desktops to enterprise-level cloud systems.
I remember upgrading my aging laptop from a SATA SSD to an NVMe drive — and it was like night and day. My system booted in under 10 seconds. Photoshop launched before I could blink. It felt like I had unlocked a whole new level of performance.
History of NVMe
While it might feel like a new invention, it has been in the making for over a decade.
The journey began with the need for a faster interface to connect SSDs. SATA, the long-time standard, was created for hard drives and couldn’t keep up with SSD speeds. So, the tech industry came together to create a protocol that would finally unleash the full power of solid-state storage.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Conceptualization | Industry experts identified need for flash-optimized interface |
| 2011 | 1.0 Released | First official specification published |
| 2014 | Widespread Adoption Begins | PCIe-based SSDs start hitting the consumer market |
| 2018 | 1.3+ | Enhanced features including power management |
| 2021+ | NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) | Enterprise-level remote access via network protocols |
As more devices needed faster data access — from cloud computing systems to gaming consoles — it emerged as the solution that finally broke the data bottleneck.
Types of NVMe

NVMe M.2
This is the most common consumer-grade form factor. It’s a small, gumstick-shaped drive that plugs directly into the motherboard. These are loved by gamers and creatives for their blazing speed and compact design, ideal for laptops and desktops alike.
NVMe U.2
U.2 drives are commonly found in enterprise environments. They offer larger storage capacities and better thermal performance, making them perfect for servers and data centers that demand reliability and volume.
NVMe Add-in Card (AIC)
These drives come in the form of PCIe expansion cards. They often include larger heatsinks for cooling and are used in high-performance desktops or workstations that need extreme storage bandwidth.
NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF)
This is the cutting-edge form of system designed for remote storage access in cloud or virtualized environments. It uses network protocols to extend its speeds over Ethernet or Fibre Channel, ideal for enterprise infrastructures.
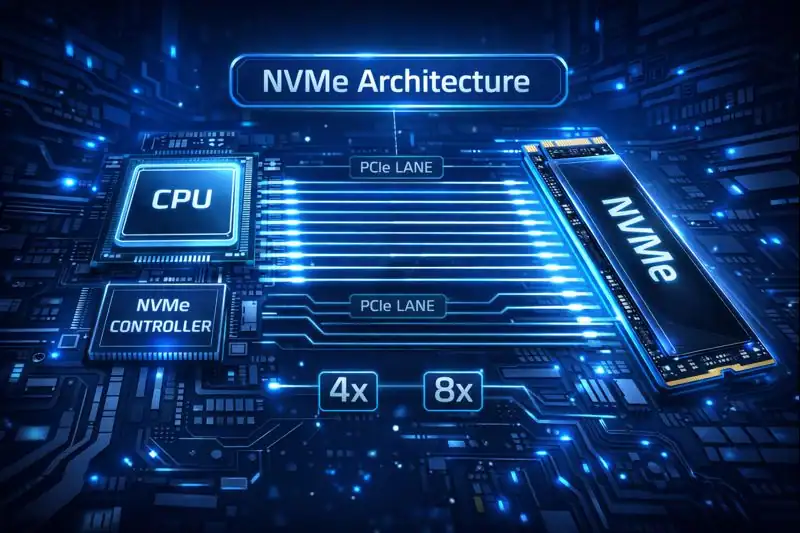
How Does NVMe Work?
When your computer requests a file — say a 4K video — it springs into action. Unlike traditional SATA protocols that only allowed one command at a time per queue, it uses thousands of parallel queues and commands. This means it can process multiple requests simultaneously without delay. NVMe communicates with the CPU directly via PCIe lanes, drastically reducing latency. All of this results in a seamless user experience where programs launch instantly, games load faster, and file transfers happen in the blink of an eye.
Pros & Cons
It brings a new standard of speed and efficiency to the table, and for many users, the upgrade is worth every penny. But like any tech, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Some older systems may not support NVMe, and the performance gains might be overkill for casual users.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Blazing-fast read/write speeds | More expensive than SATA SSDs |
| Lower power consumption | Compatibility issues with older hardware |
| Supports heavy multitasking | Generates more heat under load |
| Ideal for gaming, video editing, and virtualization | Not always necessary for basic users |
Uses of NVMe
It is more than just fast storage — it’s a foundation for many high-performance workflows and applications across industries.
Gaming and Creative Work
Gamers and content creators benefit immensely from NVMe. Games load faster, high-res assets render quicker, and video projects export in a fraction of the time. It’s a must-have for real-time, resource-intensive tasks like 3D modeling or game development.
Business and Productivity
For professionals juggling spreadsheets, databases, and multitasking apps, it delivers smoother performance. It’s particularly useful in environments with frequent read/write operations, such as accounting software, large presentations, or customer databases.
Enterprise and Cloud Infrastructure
It is critical in the backbone of modern cloud storage systems. It provides the low latency and high bandwidth necessary to serve millions of data requests per second — especially with emerging technologies like AI and machine learning.
Resources
- Tom’s Hardware – What Is It and How Does It Work.
- Intel – SSD Explained.
- Kingston – SATA SSD.
- TechTarget – NVMe Storage Definition.
- Western Digital – What is NVMe?.
