At first glance, it feels like magic artificial intelligence recreating faces and voices so convincingly that they seem real. But behind that magic lies a mix of innovation, creativity, and controversy. From Hollywood visual effects to malicious misinformation, they are changing how we perceive truth online.
Understanding what is deepfake isn’t just for tech experts anymore; it’s crucial for anyone living in the digital age. Whether you scroll through TikTok, watch YouTube, or consume the news, this technology is silently shaping your world.
What Is a Deepfake?
At its core, they are piece of media usually a video or audio clip generated or altered using artificial intelligence. The word itself blends “deep learning” and “fake.” It refers to synthetic content created through machine learning models that can convincingly mimic real people.
In simple terms, they use advanced neural networks to swap faces, clone voices, or animate still images. They can be realistic enough to trick even trained eyes, especially as the technology improves every year.
Some are harmless fun think of apps that let you “star” in a famous movie scene. Others, however, can be used for fraud, misinformation, or defamation. That’s why understanding and its implications has become so vital.
Breaking Down Deepfakes
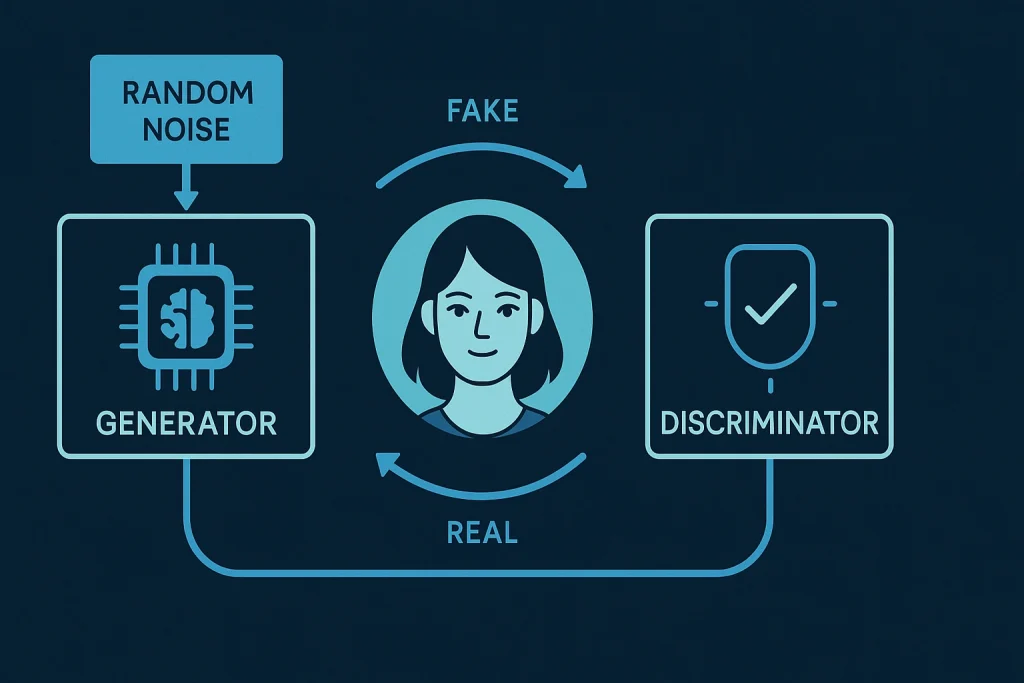
Data Collection
It begins with massive datasets of images, videos, and voice recordings used to train advanced AI models. The more diverse and high-quality the data, the more realistic the generated output becomes. Some datasets are sourced from public videos or social media, while others are synthetically generated to fill gaps.
Neural Networks and GANs
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are at the heart. One neural network (the generator) creates fake content, while another (the discriminator) evaluates its authenticity. Together, they improve until the fake becomes indistinguishable from the real thing.
Output Rendering
With powerful GPUs and optimized rendering software, a realistic video that once took days to process can now be created in hours or even minutes. Modern tools also add post-processing effects like shadow correction, lip synchronization, and background blending to enhance realism further.
History of Deepfakes
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Early CGI | Films like Jurassic Park showcased digital realism. |
| 2014 | GANs Introduced | Ian Goodfellow developed Generative Adversarial Networks, paving the way for deepfakes. |
| 2017 | Deepfakes Emergence | The term appeared on Reddit, where users began swapping celebrity faces. |
| 2019 | Social Media Crackdown | Platforms like Twitter and Facebook began restricting deepfakes content. |
| 2020s | Legal and Ethical Debates | Governments worldwide started drafting deepfake-related laws. |
Types of Deepfake
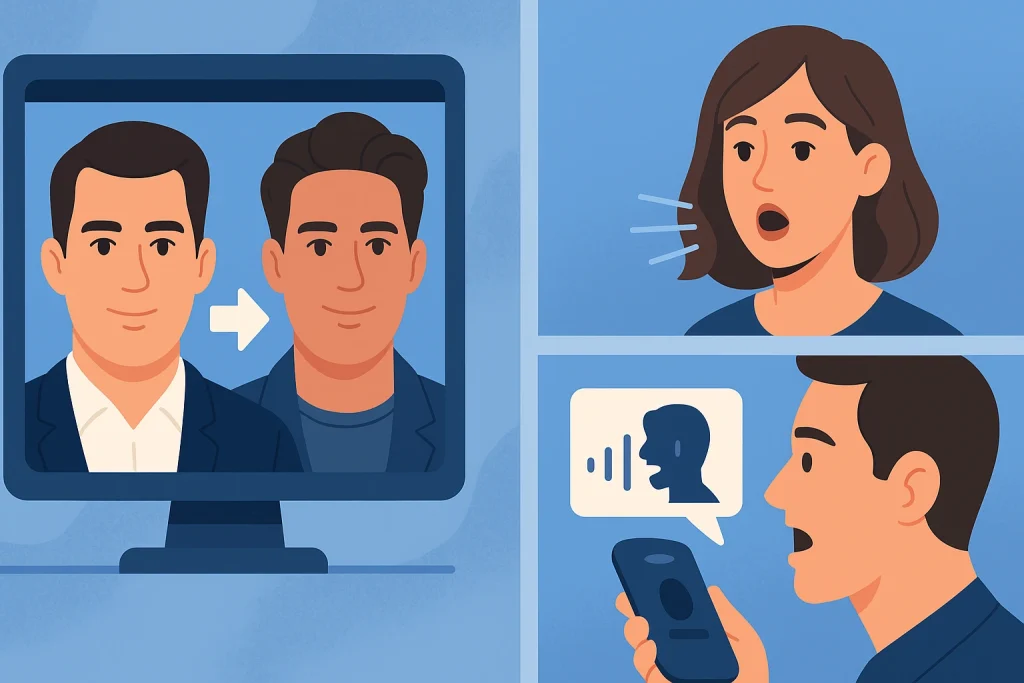

Face-Swap Deepfakes
In face-swap, artificial intelligence seamlessly replaces one person’s face with another’s in videos or photos. they are so advanced that even experts can struggle to distinguish them from real footage. The technology relies on detailed facial mapping, light adjustment, and pixel blending.
Voice Deepfakes
Voice deepfakes take things a step further by cloning speech patterns, tones, and accents using AI-driven voice synthesis. Scammers have exploited this to impersonate. However, in legitimate use cases like accessibility tools or movie dubbing voice also have shown positive potential.
Lip-Sync Deepfakes
It’s an advanced form of visual deception that uses facial tracking and 3D animation techniques. These have been used in entertainment to recreate historical figures or update dialogue in old footage, but they’ve also been misused to spread disinformation.
Full-Body Deepfakes
Using motion capture technology and neural rendering, AI can replicate human gestures, posture, and even walking style. Yet, these same capabilities raise concerns about identity theft and consent, as it becomes increasingly possible to fabricate a video of someone doing or saying anything at all.
How Do Deepfakes Work?
The process behind it creation can seem complex, but it’s essentially about teaching a computer to imitate.
First, an AI model is trained with thousands of images or video frames of the target person. Then, using deep learning, the AI learns facial movements, expressions, and angles. Next, the system maps this data onto another person’s body or voice.
Once processed, it outputs a fully synthesized clip one that looks and sounds authentic. Tools like DeepFaceLab and FaceSwap have made this process accessible even to non-experts.
Pros & Cons
Like most innovations, the technology has both benefits and drawbacks.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enhances entertainment and visual effects | Enables misinformation and fraud |
| Revives historical figures for education | Raises ethical and privacy concerns |
| Aids accessibility (e.g., voice cloning for speech-impaired users) | Can be weaponized for political manipulation |
| Drives AI research and creative tools | Challenges media trust and authenticity |
| Useful in film and gaming | Legal frameworks still catching up |
Uses of Deepfakes
Entertainment and Film
indie filmmakers are also leveraging to cut down production costs, eliminate the need for reshoots, and experiment with creative narratives. Deepfake tools are democratizing film production, making cinematic-level quality more accessible to creators everywhere.
Education and Training
In corporate training, companies are using deepfake-based simulations to prepare employees for real-world scenarios such as customer service interactions or ethical dilemmas without actual risk. By creating realistic virtual personas, learners can practice communication and decision-making in lifelike environments.
Accessibility and Assistive Tech
Voice synthesis powered by AI is now helping people who’ve lost their ability to speak regain their voices. For example, tools like Respeecher use machine learning to create personalized voice models based on old recordings. When used ethically, deepfake tools can enhance inclusivity, giving people new ways to express and experience the world around them.
Marketing and Advertising
Brands now create hyper-personalized ads where digital avatars directly address customers by name, tailoring messages to individual preferences. Deepfake-driven campaigns are pushing creativity further by allowing brands to blend reality and imagination, creating unforgettable marketing experiences.
Cybersecurity and Ethics Research
By studying how these fake videos are created, analysts can improve defense mechanisms that identify inconsistencies in pixels, lighting, or audio synchronization. This ongoing research is helping to shape the future of digital responsibility, ensuring that AI innovation remains grounded in ethical frameworks.
Resources
Deeptrace Labs: The State of Deepfakes Report
IBM: Deepfake Detection Research
BBC Future: The Rise of Deepfake Technology
Forbes: How Deepfakes Are Changing Media
MIT Technology Review: Deepfake Ethics and Regulation
