The world of technology moves fast — like, blink-and-you’ll-miss-it fast. And one of the most electrifying upgrades recently hitting center stage in this whirlwind of futuristic technology is DDR5. Whether you’re a gamer chasing peak performance, a developer compiling massive codebases, or just someone who wants their machine to run smoother and smarter, DDR5 is the memory revolution you’ve been waiting for.
Not long ago, I upgraded my desktop rig to a DDR5-compatible setup. I booted it up, launched my favorite editing software, and it felt like I had unlocked a whole new level of speed. It wasn’t just an upgrade — it was a transformation. Suddenly, everything was snappier, smoother, and surprisingly more efficient. That’s the power of DDR5, and today, we’re going to explore it from every angle — what it is, how it works, where it came from, and what it can do for you.
What is DDR5?
Let’s start with the basics. DDR5, or Double Data Rate 5, is the fifth generation of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) used in computers and servers. It’s the direct successor to DDR4, offering more bandwidth, greater efficiency, and a smarter approach to power and performance.
You might also hear DDR5 referred to as next-gen memory, RAM (Random Access Memory) upgrade, or fifth-gen SDRAM. But whatever you call it, one thing’s for sure: DDR5 is engineered to meet the growing demands of our increasingly complex digital lives — from gaming and AI to 4K video editing and data-intensive applications.
Breaking Down DDR5
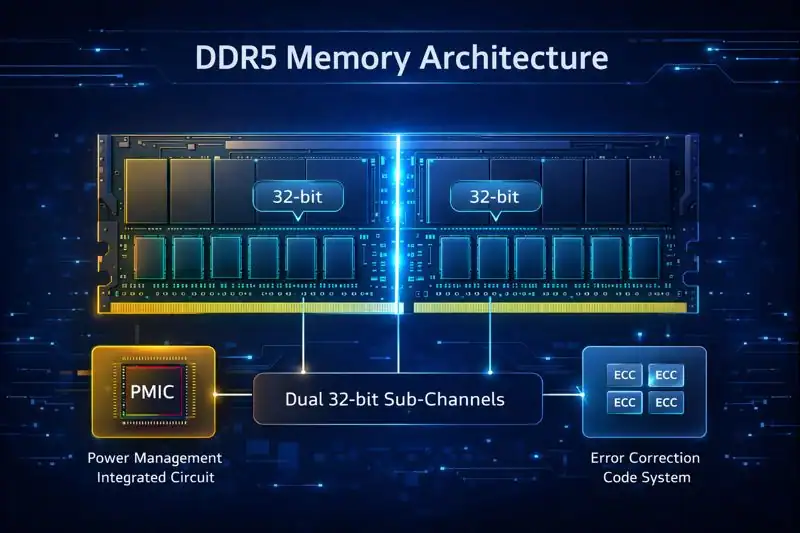
So, what makes DDR5 tick?
To understand its impact, let’s break it down into its core components:
- Higher Bandwidth
DDR5 starts with blistering data rates — beginning at 4800 MT/s and scaling up to 8400 MT/s and beyond. Compared to DDR4, that’s a massive jump. For everyday users, this means apps open faster, files transfer quicker, and games run smoother. - Increased Capacity
With support for up to 64GB per module, DDR5 delivers a quantum leap in capacity. Think about it: editing massive 8K videos, training AI models, or running multiple virtual machines becomes less of a strain and more of a breeze. - Improved Power Efficiency
DDR5 operates at just 1.1 volts, down from DDR4’s 1.2V. That may not sound like much, but over time, it means reduced heat and better energy savings — especially important for laptops and data centers. - Smarter Architecture
It introduces on-die ECC (error correction code) and dual 32-bit sub-channels. What does that mean for you? Better stability, fewer crashes, and smoother multitasking — even during high-load operations.
It’s like comparing a fuel-efficient sports car with a gas-guzzling sedan: you’re getting more speed, better control, and higher efficiency with DDR5.
History of DDR5
Like all great inventions, it stands on the shoulders of giants. Here’s a quick look at its evolution:
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2000 | DDR SDRAM makes its debut, marking the beginning of fast, double-data-rate memory. |
| 2003 | DDR2 hits the scene with better speed and lower power use. |
| 2007 | DDR3 launches with higher clock speeds and lower voltage. |
| 2014 | DDR4 becomes mainstream, supporting bigger memory modules and efficiency. |
| 2020 | It is officially announced by JEDEC, promising massive improvements. |
| 2021–2022 | Hardware manufacturers begin releasing DDR5-compatible CPUs and motherboards. |
| 2023+ | It becomes the new standard in high-end consumer and enterprise computing. |
This steady climb reflects not just progress, but an ongoing response to the exponential growth in processing needs — thanks to new inventions in gaming, cloud computing, AI, and more.
Types of DDR5

Just like cars, not all DDR5 modules are the same. Let’s explore the different variants that exist in today’s market.
For Desktops
Designed for performance-focused home and professional users, these sticks often come with heatsinks, customizable RGB lighting, and XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) support. Gamers and creatives love these modules.
For Laptops (SO-DIMM)
Smaller in form, but mighty in power. SO-DIMM DDR5 modules are crafted for compact devices like ultrabooks and gaming laptops, bringing the speed of DDR5 into portable form.
For Servers (ECC Registered)
Used in enterprise environments, these modules include ECC (Error-Correcting Code) and are registered (buffered) for stability. Ideal for mission-critical systems like databases or cloud servers.
How Does DDR5 Work?
Let’s break it down simply:
Step 1:
When you open an app or game, your CPU asks the RAM to fetch and hold the data that’s needed quickly. DDR5, with its high-speed sub-channels, kicks in and delivers that data with lightning-fast accuracy.
Step 2:
The memory controller inside your CPU communicates with it through dedicated channels. Thanks to its dual-channel sub-architecture, the data is split and processed in parallel — doubling efficiency.
Step 3:
The built-in Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) in it handles power distribution, ensuring each part of the memory gets what it needs without wasting energy.
Step 4:
On-die ECC continuously checks for errors and corrects them in real-time, ensuring stability even when workloads are heavy.
It’s a seamless dance of speed, efficiency, and precision — exactly what modern users demand in the era of Innovation.
Pros & Cons
Every new technology has its strengths and trade-offs. Here’s a balanced look at DDR5:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Significantly faster data rates | Higher initial cost |
| Supports larger memory capacity | Limited compatibility with older systems |
| Better energy efficiency | Slightly higher latency (in early models) |
| On-die ECC for improved stability | Availability may vary depending on region |
| Future-proof for modern systems | Requires new CPUs and motherboards |
In short, the ram is a powerhouse — but you’ll need to plan your upgrade carefully.
Uses of DDR5
You might be wondering: “Is DDR5 right for me?” If you value speed, stability, and future-readiness — the answer is a big yes. Let’s explore where it shines brightest.
High-End Gaming
Modern AAA games are memory-hungry. With that, frame rates get a boost, loading times shrink, and overall responsiveness improves. Pair it with a top-tier GPU, and you’re in for a buttery-smooth ride.
Example: Competitive gamers using it paired with Intel’s 13th-gen CPUs report noticeable performance lifts in games like Cyberpunk 2077 and Call of Duty.
Content Creation
From editing massive video files to rendering 3D models, creative workflows demand high-speed, high-capacity memory. It handles these tasks with grace, helping professionals meet tight deadlines.
Example: Filmmakers using Adobe Premiere Pro benefit from faster scrubbing and export times.
Data Science & Machine Learning
Training AI models requires vast memory and stable data throughput. It is built for this. With high bandwidth and capacity, data scientists can analyze large datasets faster and more reliably.
Example: AI developers training neural networks can process more data per second without bottlenecks.
Enterprise Servers
In the server world, reliability and performance are non-negotiable. The component’s modules with ECC deliver both, making them perfect for data centers and cloud computing infrastructures.
Example: Companies running iot devices across smart grids need stable, fast memory to handle real-time data streams.
Resources
Explore more about the component from the top experts and trusted sources in the industry:
- Crucial – Everything you need to know
- Tom’s Hardware – DDR5 vs. DDR4
- Intel – DDR5 Memory Support
- Corsair – Memory Matters
- JEDEC – DDR5 Standard
