Imagine a world where robots handle the most complex tasks, from assembling cars to assisting in daily life. Tesla Robotics is turning this vision into reality, pushing the boundaries of advanced technology and automation. With Tesla’s expertise in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, its robotic systems are designed to redefine industries.
From humanoid robots like Optimus to automated manufacturing lines, it is at the forefront of innovation. But what exactly is Tesla Robotics? How does it work? And what impact will it have on our future? In this blog, we’ll break down Tesla Robotics, explore its history, different types, working mechanisms, advantages, and real-world applications. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an entrepreneur, or just curious about the future of robotics, this guide will provide you with everything you need to know.
What is Tesla Robotics?
Tesla Robotics refers to the robotic automation solutions developed by Tesla Inc., aimed at enhancing efficiency, productivity, and safety across various industries. At its core, it integrates artificial intelligence, machine learning, and state-of-the-art engineering to develop autonomous robotic systems.
A prime example of it Optimus, a humanoid robot designed to assist with everyday tasks. Additionally, Tesla’s production lines feature robotic arms and AI-driven automation to streamline vehicle manufacturing. Tesla Robotics is not just about machines—it’s about creating intelligent, adaptive systems that can learn, evolve, and optimize processes in ways humans never could.
Breaking Down Tesla Robotics
At its foundation, Tesla Robotics is a sophisticated blend of artificial intelligence, precision engineering, and real-time perception. These core components work together to build machines that are not only efficient but also capable of adapting to their surroundings.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence serves as the decision-making engine behind Tesla’s robotics. Through machine learning, these systems can analyze data, recognize patterns, and improve their performance over time. This means the more they operate, the more effective and accurate they become.
Automation and Robotics Engineering
Tesla’s robots are designed with advanced engineering that allows them to carry out complex tasks with minimal human intervention. Their mechanical structures are built to perform with precision, enabling them to complete both repetitive and delicate operations in manufacturing and service environments.
Neural Networks and Computer Vision
These technologies enable Tesla robots to understand and interpret the world around them. Neural networks process large amounts of information to help with decision-making, while computer vision allows the robots to identify objects, people, and spaces. This capability is essential for safe navigation and for performing tasks in dynamic environments.
Together, these systems form the technological backbone of Tesla Robotics. They allow each machine to operate intelligently, adapt to changing conditions, and continuously learn from real-world experience. This integration not only enhances productivity but also positions Tesla at the forefront of robotic innovation.
History of Tesla Robotics
Tesla’s journey into robotics began with automation in its Gigafactories. The company leveraged robotic arms and AI-driven systems to streamline EV production. Over time, Tesla expanded its focus, introducing humanoid robotics with the announcement of Optimus in 2021.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2016 | Tesla integrates advanced robotics into its Gigafactories. |
| 2020 | AI-driven automation enhances vehicle assembly. |
| 2021 | Elon Musk unveils Tesla Optimus, a humanoid robot. |
| 2023 | Optimus demonstrates walking, lifting, and object recognition. |
| 2024 | Tesla announces further AI advancements for industrial and consumer robotics. |
The evolution of it reflects the company’s vision of making AI-powered robots an integral part of everyday life.
Types of Tesla Robotics
Humanoid Robots
Tesla’s humanoid robots, particularly Optimus, are built to mirror human movement and interact with their surroundings. These robots can walk, lift items, and execute basic tasks, making them suitable for use in homes, factories, and offices. Their versatility allows them to support labor-intensive environments and assist in routine domestic responsibilities.
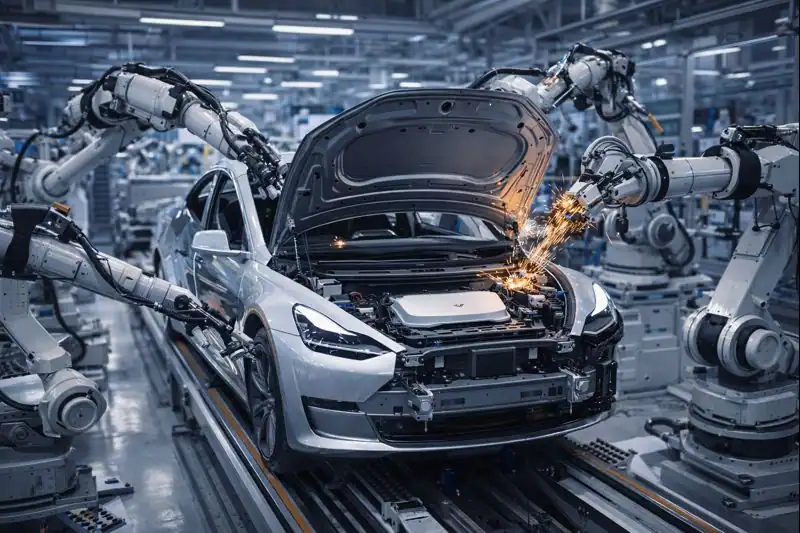
Industrial Automation Robots
Tesla’s industrial robots are critical components of its automated manufacturing process. These include robotic arms that perform welding, painting, and part assembly with precision and consistency. The integration of these robots has drastically improved the quality and speed of production in Tesla’s Gigafactories.
Autonomous Driving Systems
Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology exemplifies robotic intelligence applied to transportation. These AI-driven systems analyze real-time data to make split-second driving decisions. Although not physical robots in form, they perform autonomous functions that mirror robotic capabilities in navigation and responsiveness.
Warehouse & Logistics Robots
In Tesla’s supply chain, warehouse and logistics robots play a key role in handling materials efficiently. These robots can transport, sort, and store components within industrial spaces. Their use helps optimize inventory management and reduces dependency on human labor for repetitive tasks.
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Humanoid Robots | General-purpose tasks, assistance, labor support. |
| Industrial Robots | Vehicle assembly, factory automation. |
| Autonomous AI Systems | Self-driving technology, navigation. |
| Logistics Robots | Warehouse automation, material transport. |
How Does Tesla Robotics Work?

It operates through a combination of AI, machine learning, and advanced hardware. The robots utilize Tesla’s neural network technology to process real-world data, recognize patterns, and make decisions. Optimus, for instance, is equipped with Tesla’s self-driving AI, which enables it to understand its surroundings and perform complex movements.
Tesla’s robotics also integrate computer vision to detect objects and people, ensuring seamless interaction with their environment. Whether assembling a vehicle or walking through a warehouse, Tesla robots function autonomously, constantly improving through AI-driven learning.
Pros & Cons
Tesla Robotics presents both opportunities and challenges.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enhances efficiency and productivity. | High development and maintenance costs. |
| Reduces human labor in hazardous environments. | Potential job displacement in some industries. |
| AI-driven learning enables continuous improvement. | Ethical concerns regarding AI autonomy. |
| Can revolutionize multiple industries. | Complex regulatory challenges. |
Tesla Robotics is a game-changer, but like all innovations, it must overcome hurdles to achieve widespread adoption.
Uses and Applications
Vehicle Manufacturing
Tesla Robotics is transforming vehicle manufacturing through precision automation. Robotic arms manage complex assembly operations, from component installation to quality checks. This not only boosts production speed but also enhances safety by minimizing manual involvement in hazardous tasks.
Home & Personal Assistance
The Optimus robot is envisioned to assist individuals at home by performing daily chores. This includes fetching items, cleaning, or even helping the elderly with mobility. By handling mundane tasks, it allows users to focus more on meaningful or creative activities.
Warehouse Management
Tesla’s warehouse robots streamline inventory control by automating the handling of goods. These robots move freely across storage facilities, reducing delays and human error. Their accuracy ensures smoother workflows in Tesla’s logistics network.
Autonomous Navigation
Full Self-Driving systems enable Tesla vehicles to operate with minimal human input. Using sensors and machine learning, these systems interpret the environment and make decisions in real time. This not only enhances road safety but also paves the way for a driverless future.
Healthcare and Elderly Care (Future Potential)
In the future, Tesla Robotics could be deployed in medical and eldercare settings. These robots could assist with lifting patients, delivering medicines, or offering mobility aid. Their application would reduce caregiver workload and provide consistent, reliable support.
Construction and Infrastructure
Tesla may expand into construction robotics to perform labor-intensive duties like carrying materials or conducting inspections. Robots could improve safety by taking over dangerous tasks and working continuously without fatigue. This would mark a major leap in the efficiency of construction projects.
Education and Training
Tesla robots might also serve as tools for learning and development. They can provide hands-on demonstrations, help with technical training, or simulate real-world applications in classrooms. This could enhance the teaching of STEM subjects and vocational skills.
Resources
- Medium. Tesla: Redefining Industry as the World’s Largest Robotics
- Robotics Tomorrow. 2022 Top Article – How Tesla Used Robotics to Survive
- The Chic Icon. The Future is Now: Tesla Bot Revolutionizes Everyday Life
- Maxiom Technology. Development in Emerging Tech: Tesla’s Innovative Success
- CleanTechnica. Automating Intelligently Is Tesla’s Manufacturing Advantage
