In the ever-changing world of technology trends, few innovations have reshaped data management like Snowflake. As businesses collect massive amounts of data daily, finding efficient, scalable, and cost-effective solutions has become essential. That’s where Snowflake comes in — a cloud-based platform that revolutionizes how companies store, analyze, and share data.
I still remember working on a project where traditional databases just couldn’t keep up. The data loads were too large, queries too slow, and collaboration between departments was a nightmare. Then we switched to Snowflake, and everything changed. The speed, scalability, and simplicity were remarkable. It wasn’t just a new tool — it was a whole new way of thinking about data.
What Is Snowflake?
It is a cloud-based data warehousing platform that allows organizations to manage, analyze, and share massive datasets efficiently. Unlike traditional data warehouses that rely on on-premise servers, Snowflake runs entirely in the cloud — supporting popular services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
It’s designed to handle structured and semi-structured data while maintaining high performance and near-infinite scalability. Businesses use it to centralize their data, making insights easier to access across teams. Because it separates computing from storage, multiple users can query data simultaneously without performance drops.
In simpler terms, think of it as your company’s intelligent data brain — one that processes information faster, stores it more efficiently, and helps teams make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Breaking Down Snowflake
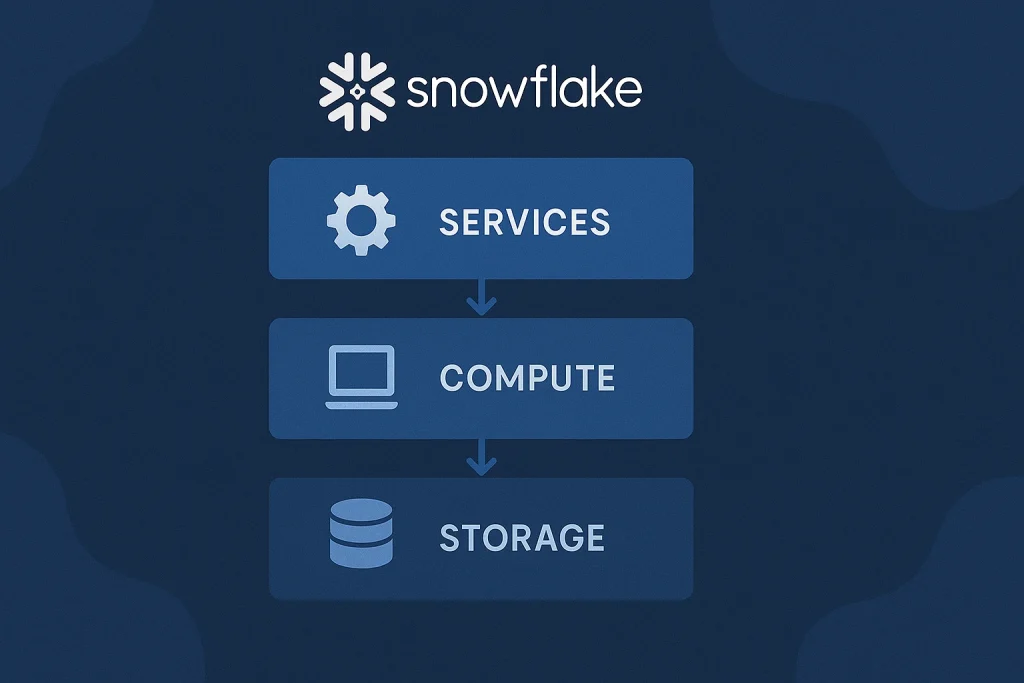
Let’s break down Snowflake into its key components. The platform’s architecture is built around three main layers: storage, compute, and services.
- Storage Layer: This is where all data is securely stored in compressed and optimized formats. You can think of it as the warehouse shelves — neatly organized and easy to access.
- Compute Layer: This handles all the queries and processing. Each compute cluster, called a “virtual warehouse,” works independently, allowing different teams to run workloads without interfering with each other.
- Services Layer: This acts as the brain of the operation, managing authentication, metadata, optimization, and transactions.
For example, when a marketing team analyzes campaign data while the finance department runs forecasts, both can do so at full speed without slowing each other down. This flexibility makes Snowflake one of the most innovative platforms in data engineering.
History of Snowflake

Snowflake was founded in 2012 by Benoît Dageville, Thierry Cruanes, and Marcin Żukowski — three data experts who saw the limitations of traditional data warehousing. Their vision was to create a cloud-native solution that broke away from the constraints of on-premise systems.
By 2014, the company emerged from stealth mode, and within a few years, it attracted major investors and enterprises. The real turning point came in 2020, when it went public in one of the largest software IPOs in history. Its success marked a new era in cloud data management, inspiring businesses to modernize their infrastructure.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2012 | Founding | Snowflake is founded by three data engineers with a vision for a cloud-native warehouse. |
| 2014 | Public Launch | The company officially launches its first version of the platform. |
| 2019 | Global Expansion | Expands to multiple cloud providers, improving accessibility. |
| 2020 | IPO | One of the largest IPOs in software history, raising billions. |
| 2024 | Continued Growth | Recognized as a leader in cloud data and analytics platforms. |
From its humble beginnings, it has become a symbol of Innovation, reshaping how modern enterprises handle their data.
Types of Snowflake
It isn’t a one-size-fits-all platform — it offers different types of usage based on business needs and industries.
Data Warehousing
This is the most common use case. It allows companies to store and query massive datasets seamlessly, making analytics faster and more accurate.
Data Sharing
It enables secure data sharing between organizations without the need for duplication. For example, a retailer can share real-time sales data with suppliers instantly, improving collaboration and decision-making.
Data Lake Integration
With its ability to handle both structured and semi-structured data, it can act as a data lake, integrating data from multiple sources like IoT devices, APIs, or logs — all in one central repository.
Data Engineering
Developers use this technology for building data pipelines and transforming raw information into usable insights. It integrates well with ETL tools, ensuring data remains clean and consistent.
Machine Learning and AI
Snowflake’s architecture supports machine learning workloads by providing quick access to massive datasets. Data scientists can train models directly using data stored within the platform, improving efficiency and accuracy.
How Does Snowflake Work?
Understanding how Snowflake works is key to appreciating its brilliance.
- Data Loading: Users upload data from multiple sources — whether it’s CSV files, streaming data, or third-party integrations. Snowflake automatically optimizes the data for storage and performance.
- Separation of Storage and Compute: Unlike traditional systems, Snowflake’s storage and compute functions operate independently. This means users can scale compute resources up or down without affecting data storage.
- Virtual Warehouses: Each team or process can have its own virtual warehouse, ensuring no query slows another.
- Query Processing: The system uses advanced optimization techniques, caching, and clustering to deliver lightning-fast results.
- Data Sharing and Security: Snowflake’s architecture supports secure, real-time data sharing while enforcing role-based access controls for privacy and compliance.
This architecture reflects the power of advanced technology, designed for modern businesses seeking real-time insights and limitless scalability.
Pros & Cons
Every technology has its upsides and downsides, and this one is no exception. It delivers incredible flexibility and performance, but like any platform, it requires proper management and understanding to maximize its value.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Highly scalable and elastic cloud architecture | Cost can increase with heavy query usage |
| Separates storage and compute for efficiency | Requires knowledge of SQL and data modeling |
| Easy integration with major cloud providers | Limited offline access due to cloud dependency |
| Fast query performance and optimization | Complex pricing for advanced features |
| Strong security and compliance measures | Learning curve for new users |
While the pros clearly outweigh the cons, careful cost management and training are essential for long-term success.
Uses of Snowflake
The versatility of Snowflake makes it a favorite across industries. It simplifies how organizations handle data, breaking down silos and improving collaboration.
Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions use Snowflake to process transactions and analyze risk in real-time. Its scalability allows them to handle enormous data volumes securely.
Healthcare
Hospitals and research institutions rely on Snowflake for data-driven decision-making, managing patient records, and conducting predictive analytics for better healthcare outcomes.
Retail and E-commerce
Retailers use it to track customer behavior, manage inventory, and personalize shopping experiences. Its real-time analytics capabilities enhance marketing precision and boost sales.
Technology and SaaS Companies
Tech companies use Snowflake to manage product metrics, monitor user activity, and support data-driven product improvements.
Government and Public Sector
Public organizations benefit from Snowflake’s secure data-sharing capabilities, improving transparency, decision-making, and service delivery to citizens.
As the demand for futuristic technology grows, Snowflake continues to lead as a trusted data management powerhouse.
Resources
- Snowflake Official Documentation. Learn the platform’s capabilities and technical details.
- Snowflake Blog. Discover case studies and insights on data innovation.
- AWS Partner Page. Explore how Snowflake integrates with Amazon Web Services.
- Forbes Technology Council. Read about how Snowflake shapes the future of data warehousing.
- Gartner Reports. Find industry analyses and expert reviews on cloud data platforms.
