In a world where every click, message, and payment travels across the internet, keeping information secure is critical. That’s where public key cryptography steps in. If you’ve ever sent a WhatsApp message, logged into your online banking, or bought something with cryptocurrency, chances are you’ve already relied on it—without even knowing.
In this guide, we’ll unpack it in simple language. You’ll see how it works, why it’s different from older systems, the history that shaped it, and real-world applications that keep our digital lives running. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of why it is one of the most important inventions in modern computing.
What is Public key Cryptography?
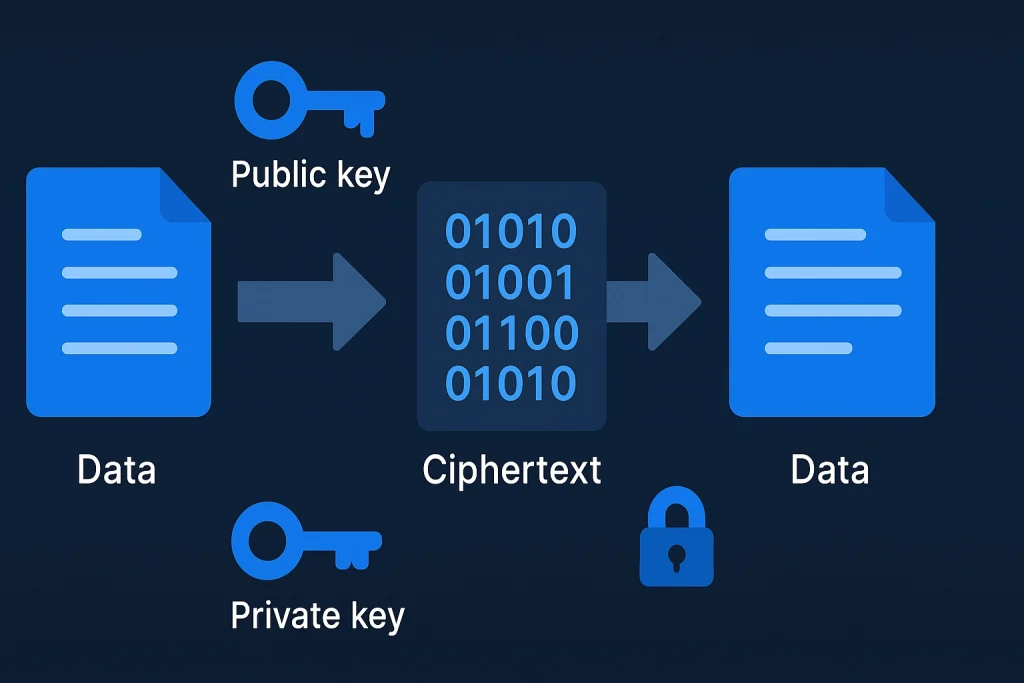
To put it simply, it is a method of securing communication that uses two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key can be shared with anyone, while the private key must remain secret. Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
This approach is also known as asymmetric cryptography, because the keys are not identical. Unlike older symmetric systems, where the same password unlocked the message for both sender and receiver, it makes it possible to communicate securely with strangers across the internet.
So, when we ask, it’s the backbone of digital trust, enabling secure exchanges without needing to hand out your personal lock-and-key.
Breaking Down Public key cryptography
The Two Keys
Think of the public key as the mailbox in front of your house. Anyone can drop a letter in, but only you, with your private key (the key to the mailbox), can unlock it. This simple idea makes private communication possible over open networks.
Encryption and Decryption
When Alice wants to send Bob a secure message, she uses Bob’s public key to lock it. Only Bob’s private key can unlock it. Likewise, Bob can sign a document with his private key, and Alice can verify it using Bob’s public key
Digital Signatures
Enables authenticity. Digital signatures prove that a message or file really came from the sender and hasn’t been tampered with. That’s how software updates from companies like Apple or Microsoft can be trusted.
Scalability
Imagine trying to share one secret password with everyone you ever meet online. Chaos, right? You don’t have to. Your public key can be widely shared, while your private key remains locked away. This makes it ideal for the massive scale of the internet.
Example: When you see the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar, it’s a sign that it is at work. It’s encrypting your data as it travels between your device and the website, shielding it from prying eyes.
History
The story is as fascinating as the system itself. While codes and ciphers have existed for centuries, the asymmetric method was first proposed in the 1970s, revolutionizing secure communication and laying the foundation for modern encryption technologies still used today.
| Period | Development in Public key cryptography |
|---|---|
| Pre-1970s | Cryptography relied on symmetric keys (same secret shared). |
| 1976 | Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman introduced the concept of public/private keys. |
| 1977 | Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman created RSA, one of the first practical systems. |
| 1990s | Adoption expanded with SSL/TLS for secure websites. |
| 2000s–2020s | Became the backbone of blockchain, messaging apps, and online security. |
Types of Public key cryptography
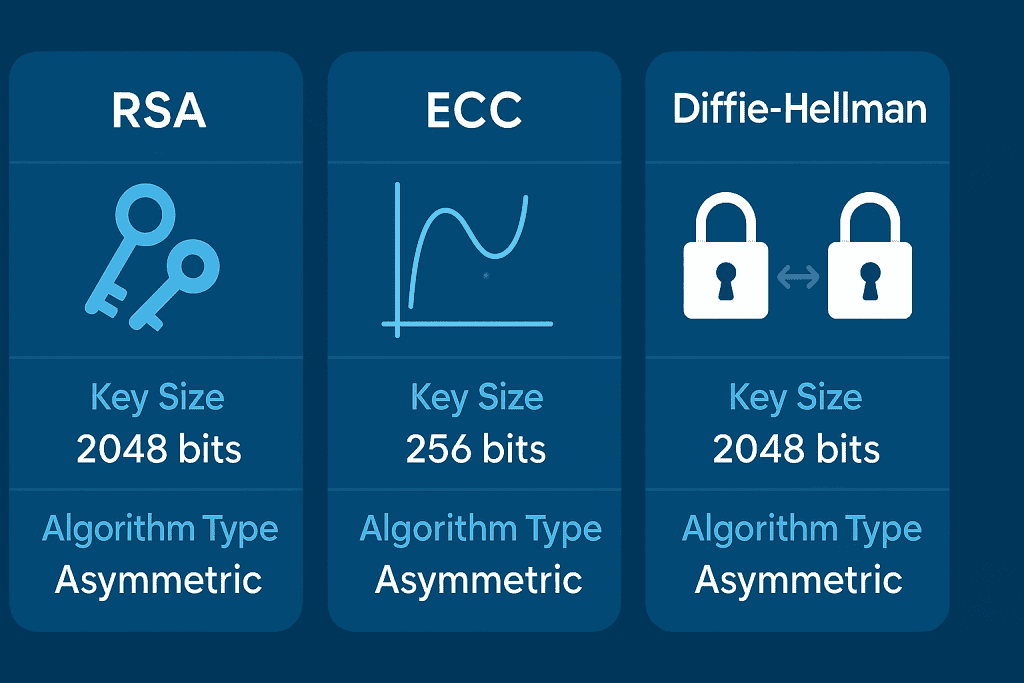
There are several types of each designed for different purposes.
RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman)
One of the earliest and most widely used asymmetric encryption algorithms, ideal for secure communication and digital signatures.
ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
A more modern public key system that achieves the same cryptographic security with smaller keys, making it faster and more efficient.
Diffie–Hellman
Primarily used for secure key exchange, allowing two parties to establish a shared secret over an untrusted network.
DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)
Focused on digital signatures, ensuring authenticity, integrity, and verification of data.
How does Public key cryptography work?

The process begins when a pair of keys is generated: one public, one private. You share the public key freely, but you keep the private key secret. If someone wants to send you a secure message, they encrypt it using your public key. Only your private key can decrypt it. Likewise, if you sign something with your private key, others can verify the signature using your public key.
In short, it works by creating a lock-and-key relationship that ensures both confidentiality and authenticity, giving users trust, privacy, and confidence when communicating or exchanging data across open digital networks.
Pros & Cons
Like any system, it has strengths and weaknesses.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Enables secure communication over open networks | Slower than symmetric cryptography |
| Supports digital signatures and trust | Requires more computing power |
| Scales well for large systems like the internet | Vulnerable if private key is compromised |
| Essential for blockchain and SSL/TLS | Complex math may be hard to explain |
Uses of Public Key Cryptography
It ensures that your online payments remain private, your emails can’t be forged, your software updates are trustworthy, and your blockchain transactions are verifiable.
Web Security
SSL/TLS certificates use it to encrypt web traffic, making sure the information you send to a website—like credit card details or login credentials—cannot be intercepted by attackers. It creates the foundation of secure browsing, turning the open internet into a safer place for banking, shopping, and everyday communication.
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures ensure that documents, emails, and even software updates are authentic and untampered. For example, when you download an update for your operating system, digital signatures confirm it truly came from the developer and hasn’t been altered by hackers. In the business world, contracts signed digitally are now legally binding because cryptography makes them just as trustworthy as physical signatures.
Education & Tutorials
Students and developers alike can experiment with coding examples that demonstrate encryption and decryption in action. By practicing with key pairs, they learn how secure channels are built, why certain algorithms are chosen, and how these concepts power everything from messaging apps to secure voting systems. It has become a cornerstone in the education of computer science and cybersecurity.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Every crypto wallet is based on a key pair system: the public key serves as your wallet address (something you can safely share), while your private key proves ownership and allows you to spend your funds. This mechanism doesn’t just protect your money—it ensures the integrity of entire blockchain ecosystems by validating transactions and preventing fraud.
Resources
- Britannica: Public-key cryptography security
- Cloudflare: Public key cryptography Guide
- GeeksforGeeks: Public Key Encryption
- MetaSchool: Public Key Cryptography Guide
- Stanford University: Public-Key Cryptography Graduate Course
