Databases may not grab headlines like AI or blockchain, but they’re the quiet workhorses behind every digital interaction. PostgreSQL fits into this narrative by offering a balance of tradition and innovation. It’s both battle-tested and forward-looking, making it ideal for developers who want reliability without sacrificing the flexibility demanded by modern applications.
When I first encountered it, I was working on a student project. I remember battling with clunky tools that couldn’t handle complex queries efficiently. A mentor suggested this RDMBS, and suddenly, it felt like I had switched from a clumsy bicycle to a high-performance sports car. The speed, the flexibility, and the reliability were undeniable. And that personal experience is echoed by millions of developers and businesses around the world today.
What is PostgreSQL?

Think of PostgreSQL as a trusted digital vault. It not only stores your information but ensures it’s safe, accurate, and accessible whenever you need it. Unlike simpler tools that crack under pressure, PostgreSQL thrives when the stakes are high. That’s why industries ranging from healthcare to finance adopt it confidently.
it is a powerful open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). It’s known for its stability, performance, and compliance with SQL standards. Unlike some lightweight databases, PostgreSQL is feature-rich and can handle everything from small web apps to massive enterprise-grade platforms.
Also known as “Postgres,” it’s often celebrated as one of the most advanced open-source databases. Its versatility makes it a top choice for startups, Fortune 500 companies, and research institutions alike. In plain terms, if you need a dependable way to manage structured data, it has your back.
Breaking Down PostgreSQL
So, what makes it shine compared to other databases? Let’s break it down:
Tables and Rows
PostgreSQL organizes data into tables with rows and columns. This classic relational structure ensures consistency and order, which is why businesses trust it for handling mission-critical data. Imagine a library where every book is neatly cataloged, indexed, and easy to find.
ACID Compliance
Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability. These four principles guarantee that every transaction is executed correctly and safely. For example, when you transfer money between bank accounts, PostgreSQL ensures the transaction either completes fully or doesn’t happen at all. There’s no room for half-done actions or lost data, which makes it a trusted choice for financial systems, healthcare records, and enterprise apps.
Extensions
PostgreSQL allows developers to add extensions to boost functionality. A well-known example is PostGIS, which transforms it into a geospatial database capable of mapping, location tracking, and geographic analysis.
Advanced Queries
eyond simple SELECT statements, it supports joins, subqueries, window functions, and analytics across massive datasets. Whether it’s a marketing analyst pulling insights from millions of customer records or a data scientist running predictive models, PostgreSQL’s query power makes complex data storytelling possible.
Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
Instead of locking tables and forcing users to wait, MVCC creates multiple versions of data to ensure smooth transactions. This means teams can work simultaneously without interruptions, like editors working on different drafts of the same document but still preserving the integrity of the final version. For businesses running global applications, this ensures speed, reliability, and peace of mind.
History of PostgreSQL
To truly understand it, we need to step back and explore its history. Unlike trendy databases that appear and fade, it has decades of evolution behind it.
It all began in the 1980s at the University of California, Berkeley. Michael Stonebraker led the POSTGRES project, aiming to improve on the limitations of the Ingres database. By 1996, it adopted SQL as its query language, and it was officially born.
Here’s a quick timeline of its milestones:
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1986 | POSTGRES project initiated at UC Berkeley |
| 1996 | SQL support added; PostgreSQL released |
| 2000s | Rapid community growth and enterprise adoption |
| 2010s | Rise of cloud deployments and major extensions like PostGIS |
| 2020s | PostgreSQL recognized as a leading open-source RDBMS globally |
Today, it continues to evolve through a global community of developers, ensuring it remains cutting-edge in performance and functionality.
Types of PostgreSQL
It is a single database system, there are different editions and distributions tailored to unique needs.
PostgreSQL Community Edition
The free, open-source version supported by a vibrant global community. Ideal for individuals, startups, or educational projects.
PostgreSQL Enterprise Variants
Companies like EDB (EnterpriseDB) offer enhanced versions of it with added support, security features, and enterprise tools. These are favored by corporations managing sensitive or mission-critical data.
PostgreSQL in the Cloud
Cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all offer managed services. For example, Amazon RDS it allows businesses to scale quickly without worrying about server management.
PostgreSQL Extensions
This isn’t a separate type, but it deserves mention. Extensions like PostGIS turn it into a specialized tool for geospatial applications, making it invaluable for industries like mapping, logistics, and urban planning.
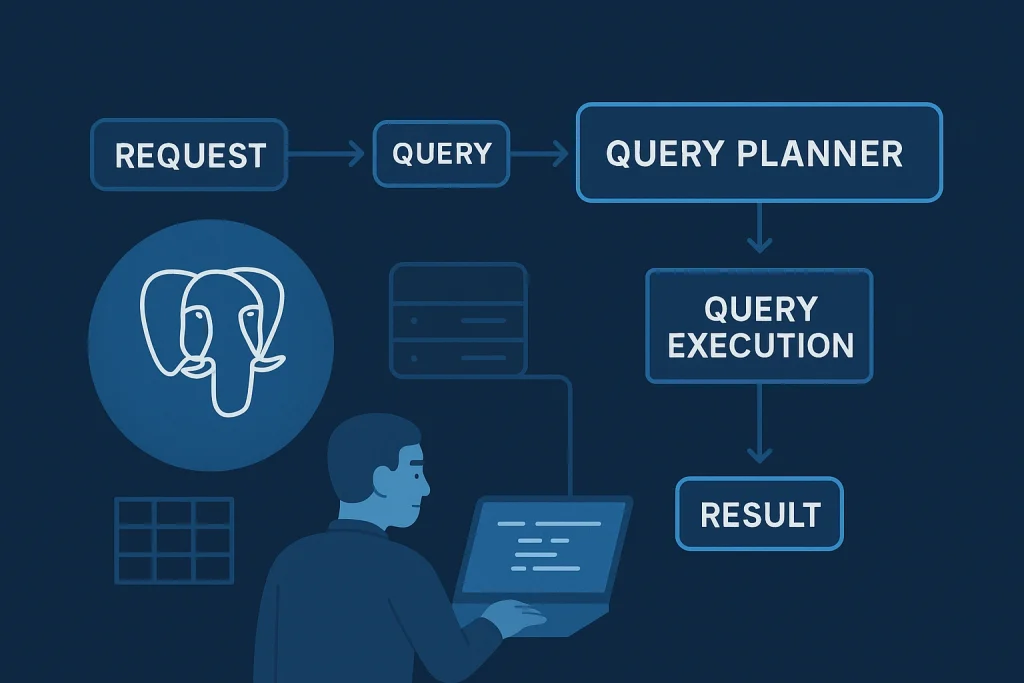
How Does PostgreSQL Work?
Understanding it isn’t complete without looking at how it functions behind the scenes.
When you send a query, it parses it, optimizes it, and executes it against stored data. The system ensures ACID compliance, so transactions are processed reliably. Thanks to MVCC, multiple users can work simultaneously without conflicts.
- Step 1: Client sends SQL query.
- Step 2: parses and optimizes the query.
- Step 3: Database engine executes the query using indexes, joins, or aggregations.
- Step 4: Results are returned almost instantly.
In addition, replication and failover mechanisms provide high availability, while sharding strategies ensure scalability. This architecture makes it capable of powering apps for small businesses and tech giants alike.
Pros & Cons
Like every tool, it has its strengths and weaknesses.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Reliable | Steeper learning curve |
| Open-source | Can be slower than specialized NoSQL |
| Scalable | Requires tuning for big workloads |
| Feature-rich | Less beginner-friendly |
| ACID compliant | Not ideal for unstructured data |
Uses of PostgreSQL
So, where does it fit into the world of technology trends? The answer is: almost everywhere.
Web Applications
From small startups to enterprise giants, it powers web apps with speed and reliability. Think e-commerce, social media, and SaaS platforms.
Financial Systems
Banks and fintech companies depend on this RDMBS for secure, compliant transactions and analytics. Its reliability makes it a favorite in this high-stakes industry.
Geospatial Applications
With PostGIS, it becomes a powerhouse for mapping and location-based services. Companies in logistics and ride-sharing rely on this feature heavily.
Data Warehousing
It handles analytical workloads, making it suitable for data warehouses and business intelligence. Its ability to process large datasets with complex queries is a major advantage.
Resources
- PostgreSQL.org: Official Documentation.
- EDB: Enterprise PostgreSQL Overview.
- AWS: Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL.
- Google Cloud: Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL.
- Microsoft Azure: PostgreSQL Flexible Server.
