The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) remains one of the most important institutions shaping the digital and technological landscape today. As an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce, NIST has played a major role in defining standards, guidelines, and best practices that help organizations build more secure, efficient, and resilient systems across industries. One of its most widely adopted contributions is the NIST CSF (Cybersecurity Framework), a flexible and comprehensive guide for managing cybersecurity risk in an ever-changing threat environment.
Understanding what NIST does — and why the NIST CSF matters — is critical for businesses, governments, researchers, and professionals who aim to align with global benchmarks and strengthen their operational resilience.
What is NIST?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology was founded in 1901 to establish measurement standards that promote consistency, fairness, and reliability across commerce and technology. While many people associate NIST with scientific measurement and calibration, its influence extends far beyond scientific labs into cybersecurity, data privacy, and risk management.
NIST operates as a non-regulatory agency whose core mission is to develop foundational standards and practices to enhance innovation and reduce uncertainty in technology systems. Its work impacts everything from cryptographic algorithms and hardware testing to national cybersecurity strategies and supply chain risk guidance.
One of the most impactful outputs from NIST in recent years has been the development of the NIST CSF, originally released in 2014 and later updated to version 2.0 to meet the demands of modern cyber risks.
Background
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) plays a significant role in the foundation of modern technology and infrastructure. Although its presence is not always visible, the standards it develops influence nearly every aspect of daily life. From communication systems and online transactions to medical equipment and transportation, NIST helps ensure these technologies perform reliably and securely.
A central part of NIST’s mission is to establish consistent measurement standards. This work is essential for eliminating discrepancies across industries and regions. Without such standards, activities like monitoring a patient’s health or conducting scientific research could produce inaccurate or conflicting results. NIST CSF provides a common framework that allows organizations to operate with clarity and precision.
In addition to its technical contributions, it actively supports innovation. It collaborates with businesses, universities, and government agencies to address complex challenges through research and applied science. These efforts lead to practical solutions that not only improve efficiency but also build public trust in emerging technologies.
History
NIST first introduced the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) in response to a 2013 U.S. executive order focused on strengthening critical infrastructure security. Since its public release in 2014, the framework quickly became a central reference for cybersecurity risk management, initially targeting sectors like energy, finance, and healthcare, but later expanding far beyond those domains.
Over time, updates to the framework — including version 1.1 in 2018 and the major revision in 2024 (CSF 2.0) — have expanded its scope, clarity, and applicability. The newest version introduces a Govern function to underscore the importance of executive involvement and strategic oversight of cybersecurity programs.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1901 | Establishment as NBS |
| 1947 | Development of the National Standard Reference Data System |
| 1977 | Advances in semiconductor metrology |
| 1988 | Renamed to NIST, expanding focus on innovation |
| 2014 | Introduction of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework |
Types of NIST CSF Standards
The National Institute of Standards and Technology’s contributions can be categorized based on their application:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity | Frameworks like SP 800-171 guide data protection. |
| Physical Standards | Measurements for scientific experiments. |
| Energy Efficiency | Standards ensuring sustainable practices. |
| Information Technology | Cryptographic standards like AES. |
How Does it Work?
NIST CSF operates through a structured, collaborative approach that turns real-world challenges into practical standards. The process begins when a specific need for standardization emerges from industry, academia, or government sectors. Once identified, NIST CSF gathers subject-matter experts and stakeholders to research the issue in depth. This research phase often includes lab testing, simulations, and field data analysis to understand what works best in practice.
After developing potential solutions, the National Institute of Standards and Technology drafts technical documents or guidelines that outline recommended approaches. These drafts are shared publicly for feedback, allowing industry professionals and researchers to contribute insights. NIST then revises and finalizes the documents based on this input, ensuring the standards are both scientifically sound and practically applicable.
Once published, organizations can adopt these standards to improve consistency, security, and compliance across their operations. Many standards also gain recognition from international bodies, making them useful for global alignment. Through this process, the NIST CSF turns complex technical needs into clear and actionable guidelines that benefit entire industries.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Promotes global consistency | Can be complex to implement |
| Enhances data security | Regular updates may pose challenges |
| Encourages innovation | May require significant resource investment |
Leading Companies Using NIST CSF
IBM
IBM integrates the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s encryption standards across its cloud security infrastructure. By doing this, the company ensures that enterprise clients benefit from reliable and advanced protection mechanisms. Its adherence to protocols demonstrates a commitment to regulatory compliance and cybersecurity excellence.
Microsoft
Microsoft follows NIST CSF to secure Azure, its cloud platform. This includes applying guidelines for data protection, identity management, and network defense. The use of these standards helps Microsoft meet the requirements of diverse industries and government regulations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services aligns with cybersecurity guidelines to enhance its cloud offerings. It uses these standards to build resilient systems that protect customer data and enable regulatory compliance. This approach assures clients of consistent, secure, and scalable solutions.
Google employs the NIST CSF techniques within its enterprise and cloud products. These techniques bolster the security of user data and ensure end-to-end encryption. By adopting standards, Google strengthens its cybersecurity framework and instills greater trust in its services.
Cisco
Cisco uses NIST standards to secure its network infrastructure products. These standards help the company detect threats early and maintain system integrity. By incorporating appropriate practices, Cisco enhances the reliability and security of communications networks worldwide.
Applications of NIST CSF Standards
Cybersecurity
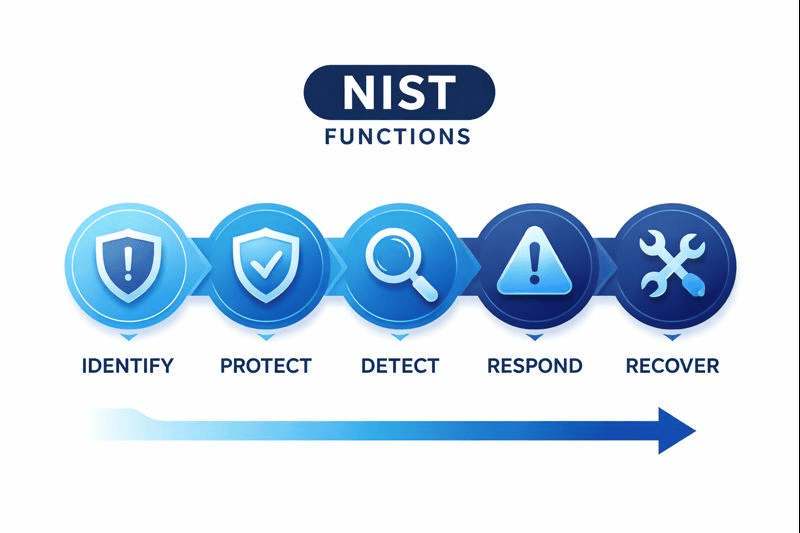
NIST CSF is widely used to identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents. Organizations implement this structured approach to manage digital risks. Its flexibility allows it to be customized across sectors and business sizes.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations use the standards of the National Institute of Standards and Technology to calibrate diagnostic devices and maintain accuracy in medical testing. These standards reduce variability in equipment performance and ensure consistent results. NIST protocols are vital in maintaining quality and safety in patient care.
Aerospace
In aerospace, precision is critical, and measurement standards provide the accuracy required. These standards support the development of satellite parts and aircraft systems. Manufacturers depend on NIST to ensure their technologies meet rigorous performance benchmarks.
Energy
Energy providers implement the standards of the National Institute of Standards and Technology to optimize smart grid technologies and enhance cybersecurity. These guidelines help protect power infrastructure from digital threats. By adopting NIST frameworks, energy companies ensure safer, smarter, and more reliable systems.
E-commerce
E-commerce platforms use the protocols of the National Institute of Standards and Technology to encrypt online transactions and protect customer data. These cryptographic standards prevent unauthorized access to payment information. As a result, businesses can offer secure online experiences and build consumer trust.
Resources
- Thales Group. What Is NIST CSF 2.0?
- IBM. What Is NIST?
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Kiteworks. What Is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
- Trend Micro. NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2024: What You Need to Know
