When you first hear the term what is digital twin, it might sound like something out of a sci-fi novel. But in reality, it’s one of the most exciting innovations in modern technology, with massive implications for industries ranging from healthcare to aerospace. At its core, it is a virtual copy of a real-world object, process, or system. This digital model is constantly updated with real-time data, meaning it doesn’t just mimic the physical—it evolves with it.
Why is this important? Imagine predicting a machine failure before it happens, testing a new building design without ever laying a brick, or even simulating how a city would respond to climate change. Understanding helps us see how organizations reduce costs, improve efficiency, and innovate faster. It’s a concept transforming industries worldwide—and it’s only just getting started.
What is Digital Twin?
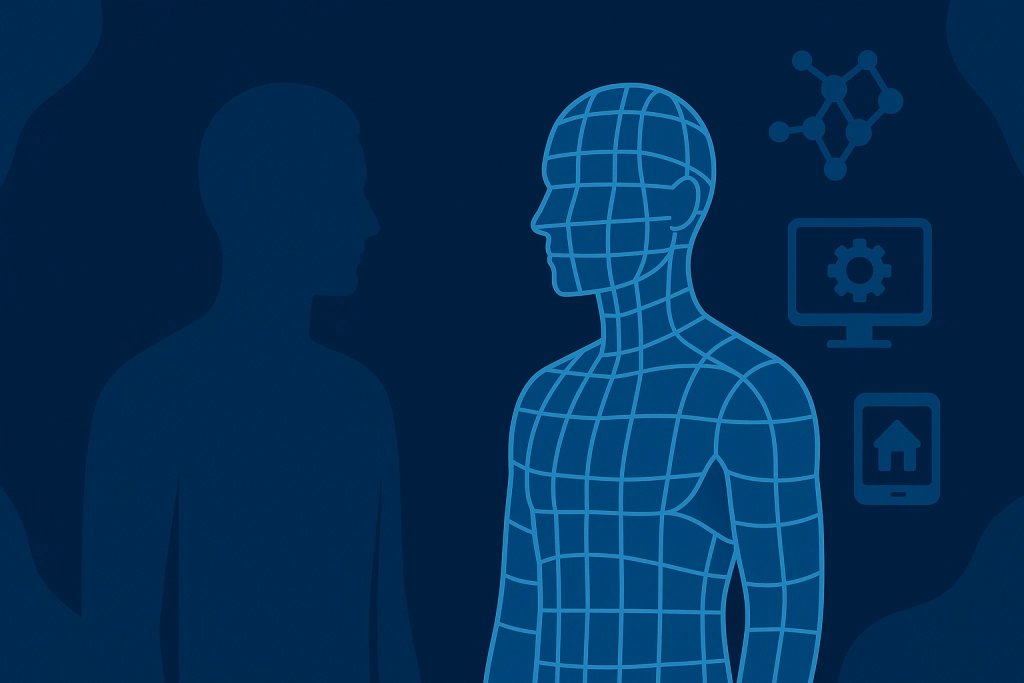
It is a virtual representation of a physical object, process, or system that mirrors its real-world counterpart in real time. Think of it as a high-tech clone, created through sensors, data streams, and advanced modeling. While the physical asset operates in the real world, its digital twin continuously updates to reflect changes, behaviors, and performance.
This technology goes beyond simple 3D modeling. It uses live data, machine learning, and IoT connectivity to simulate how an object behaves under different conditions. For example, an aircraft engine can have a digital twin that predicts wear and tear, allowing engineers to perform maintenance before a breakdown happens.
Breaking Down Digital Twin
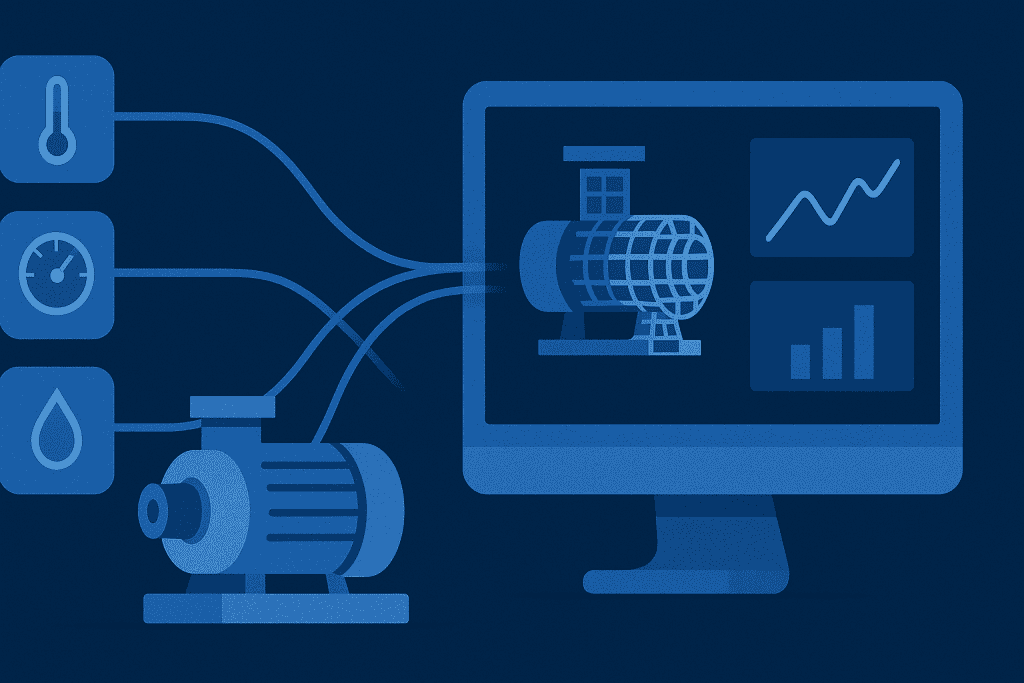
The Physical Asset
This could be a jet engine, a manufacturing plant, a human organ, or even an entire city. Anything in the real world that produces data can have a twin.
The Digital Model
The twin isn’t just a static 3D model—it’s connected to its real counterpart. Thanks to sensors, IoT devices, and cloud systems, data flows constantly into the model, making it behave exactly like the real thing.
Data & Analytics
The magic lies in the data. they don’t just mirror; they predict. By analyzing live information, companies can test scenarios—like what happens if a machine overheats or if traffic surges in a city center.
Feedback Loop
This is where things get powerful. The twin provides insights back to the physical object. For example, if it predicts engine wear, maintenance can be scheduled before breakdowns occur.
History of Digital Twin
The journey dates back several decades. NASA is credited with using the concept during the Apollo missions, creating virtual models of spacecraft to test scenarios on Earth. Over time, as computing power, sensors, and the Internet of Things (IoT) advanced, digital twins moved from space exploration into mainstream industries.
| Period | Development in What is digital twin |
|---|---|
| 1960s–1970s | NASA uses early digital twin concepts in Apollo missions |
| 1990s | Rise of simulation software and virtual modeling |
| 2000s | Digital twin term popularized by Dr. Michael Grieves |
| 2010s–2020s | Widespread adoption in manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities |
Types of digital twin

Prototype Twins
Virtual models built in the earliest stages of product design and development. They allow engineers, architects, and designers to simulate how a product will perform before investing in physical materials. Essentially, prototype twins act as a risk-free testing ground where creativity meets data-driven insights.
Instance Twins
Real-time digital copies of assets already operating in the physical world. Think of them as live digital shadows that capture performance, usage, and health data. This enables predictive maintenance—fixing small issues before they become major breakdowns. Airlines also rely on instance twins for engines, helping ensure safety while cutting maintenance costs.
Aggregate Twins
Combining data from many individual twins into a unified digital ecosystem. Instead of modeling a single machine, aggregate twins might represent an entire factory, supply chain, or even a city’s infrastructure. Aggregate twins provide a holistic view of complex networks, enabling leaders to make smarter, data-backed decisions.
Pros & Cons
Before adopting this innovation, it’s important to weigh the strengths and challenges.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Predicts failures before they happen | High cost of implementation |
| Improves efficiency and saves resources | Requires constant data collection |
| Enables better design and innovation | Concerns around privacy & security |
| Supports large-scale urban planning | Complex integration with existing systems |
How does digital twin work?
At a basic level, sensors collect data (temperature, speed, vibration, energy use) from the physical world. This information flows into cloud-based systems where it processes. AI and analytics then simulate performance, identify risks, and suggest improvements.
Finally, these insights flow back to the real asset, creating a continuous feedback loop. This constant exchange allows organizations to predict issues before they occur, optimize operations in real time, and test new strategies in a safe digital environment. The result is smarter decision-making, reduced downtime, and a system that continuously learns and adapts.
Uses of Digital Twin
Manufacturing
Digital twins have become game-changers for efficiency and reliability. By analyzing sensor data in real time, manufacturers can schedule maintenance only when it’s actually needed, cutting costs while avoiding costly shutdowns.
Beyond predictive maintenance, digital twins also help simulate workflows, optimize factory layouts, and reduce waste. This means a car manufacturer, for example, can test assembly line changes digitally, ensuring smoother operations before making any real-world adjustments.
Healthcare
This allows medical professionals to experiment with drugs, surgical techniques, and therapies in a risk-free environment before applying them in real life.
Researchers are even developing full-body digital twins that could track a person’s health throughout their lifetime, offering personalized treatments and early disease detection.
Smart Cities
Take Singapore, for example: its digital twin is used to simulate flooding scenarios, traffic congestion, and even air pollution levels, helping city planners prepare for emergencies while improving long-term infrastructure. Houston, on the other hand, leverages digital twins to monitor energy usage and optimize city services.
By mirroring the entire city in a virtual model, urban planners can test different policies—like new public transport routes—before implementation, ensuring resources are allocated wisely. This creates safer, greener, and more resilient cities for citizens.
Legal & Ethical Concerns
Digital twins rely heavily on sensitive data collection, which raises concerns about privacy, security, and ethics. How the data should be protected. In smart cities, there are worries about surveillance and the potential misuse of personal information.
Additionally, industries must consider the ethical use of AI and algorithms that power these systems. Without strong governance, there’s a risk of bias or misuse.
Conclusion
Understanding what is digital twin gives us a clearer view of how the physical and digital worlds are merging in ways once thought impossible. By creating virtual replicas of machines, systems, and even entire cities, organizations can predict failures, optimize performance, and explore endless “what-if” scenarios without the risks or costs of real-world testing.
Resources
- OpenText: Digital Twin Cases
- Coursera. What Is a Digital Twin? Definition, Types, and Uses
- Forbes. Digital Twins Used in Practice
- Reuters. Digital twin Use and Development
- Reuters. Digital twin Battle for Climate Resilience
