In the fast-moving world of technology trends, the Data Lake has emerged as a game-changer. Imagine a vast, digital reservoir that holds raw, unfiltered information from every corner of your organization—ready to be explored, analyzed, and transformed into insights. That’s exactly what a Data Lake does. It gives businesses the freedom to store massive amounts of data without forcing them into rigid structures.
This flexibility allows companies to experiment, innovate, and make smarter decisions faster. From global corporations to small startups, the adoption of Data Lakes reflects a growing need to harness the power of data in a more fluid, dynamic way. It’s one of the most influential shifts in advanced technology, shaping how we handle information in the digital age.
What is Data Lake?
A Data Lake is a centralized repository that stores raw data in its native format—structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. Unlike traditional databases that require predefined schemas, Data Lakes keep everything open and flexible. This means data can be stored exactly as it is, ready for use when needed.
Think of it like an actual lake where different rivers (data sources) flow in—customer logs, IoT data, videos, spreadsheets, and more. You can dive in at any point to extract insights without draining or reorganizing the entire system. This adaptability is what makes a Data Lake crucial for modern analytics, AI, and Innovation.
Breaking Down Data Lake
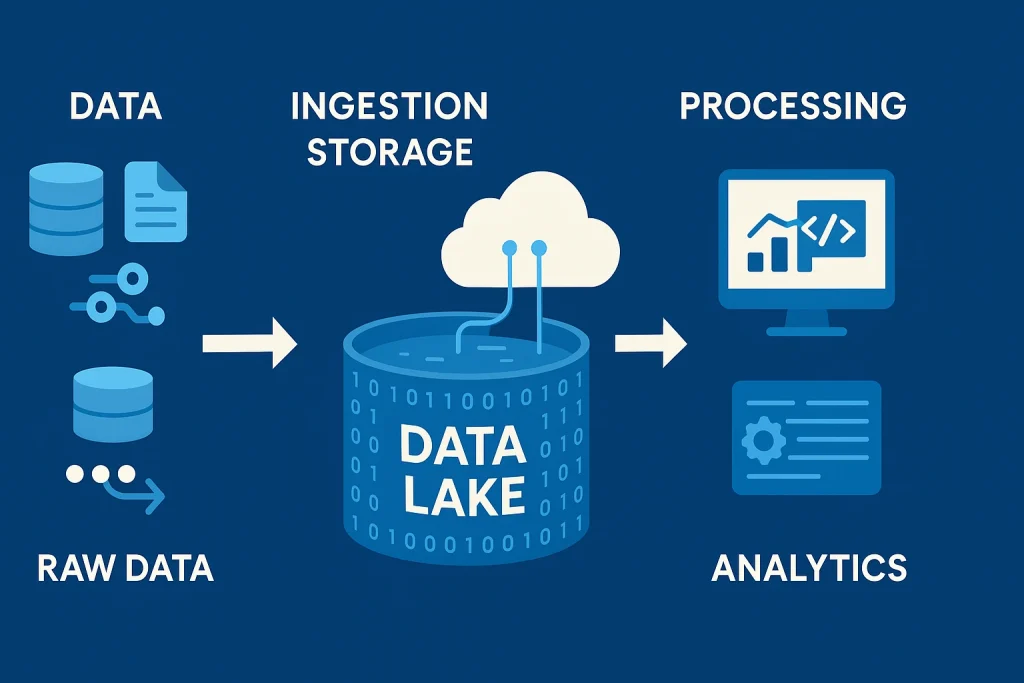
To truly understand a Data Lake, let’s break down its key components:
- Data Ingestion: The process of collecting and importing data from multiple sources such as applications, IoT sensors, and databases.
- Storage Layer: This is the foundation where all data resides, whether in cloud platforms like AWS S3 or on-premises servers.
- Metadata and Cataloging: Helps users find, understand, and manage stored data efficiently.
- Processing Framework: Tools like Apache Spark and Hadoop process the raw data into usable insights.
- Analytics and Visualization: The final stage where analysts use BI tools to interpret and visualize findings.
For example, a retail company could use a Data Lake to combine point-of-sale data, customer feedback, and website traffic—all in one place—to better predict buying behavior and improve the customer experience.
History of Data Lake
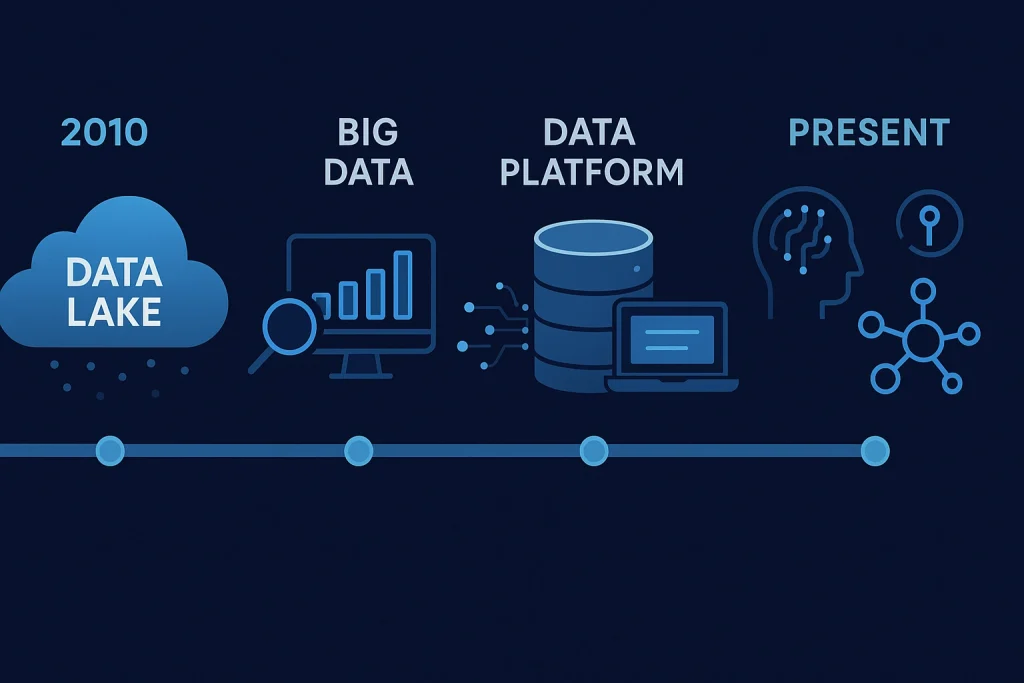
The concept of the Data Lake first emerged in the early 2010s as companies sought new ways to store and analyze the flood of big data generated by digital systems. It was born from the limitations of traditional data warehouses, which required rigid structures that couldn’t keep up with diverse modern data.
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | Term “Data Lake” coined by James Dixon (Pentaho CTO) | Introduced flexible data storage concept |
| 2012 | Big Data technologies like Hadoop gained traction | Enabled scalable data storage |
| 2015 | Cloud providers introduced managed Data Lakes | Made it easier for businesses to adopt |
| 2020–Present | Integration with AI and IoT ecosystems | Drove intelligent data analytics and automation |
As futuristic technology like machine learning and IoT became mainstream, Data Lakes evolved to handle more complex data streams and enable real-time analytics. Today, they are the foundation of intelligent decision-making in every digital enterprise.
Types of Data Lake
Cloud-Based Data Lake
Cloud Data Lakes store information on cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. They provide scalability, cost-efficiency, and seamless integration with AI and machine learning tools.
On-Premises Data Lake
These are hosted on a company’s internal servers, giving organizations full control over their data and security but requiring higher maintenance and infrastructure costs.
Hybrid Data Lake
A combination of cloud and on-premises solutions, this type offers flexibility and helps businesses balance control with scalability.
Multi-Cloud Data Lake
This newer model integrates multiple cloud platforms, ensuring redundancy, performance optimization, and resilience in case of system failures.
Each type serves different needs, depending on data privacy regulations, budget, and scalability goals.
How Does Data Lake Work?
Here’s how a Data Lake works from start to finish:
- Data Collection: Information from various sources—such as social media, IoT devices, and enterprise systems—is gathered continuously.
- Data Storage: All this data is stored in a raw, unprocessed format in the Data Lake. Unlike databases, it doesn’t require transformation before being saved.
- Data Processing: Using frameworks like Hadoop or Apache Spark, data is filtered, cleaned, and prepared for analysis.
- Data Analysis: Analysts or data scientists apply AI, ML, and visualization tools to uncover patterns and insights.
- Data Access: Authorized users can query the lake anytime to retrieve specific datasets for decision-making.
This process gives companies an edge—enabling agility, accuracy, and scalability in managing ever-growing information. It’s what makes Data Lakes the backbone of digital transformation across industries.
Pros & Cons
Before implementing a Data Lake, it’s important to weigh its advantages and challenges.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Stores all types of data in one place | Can become disorganized without proper management |
| Highly scalable and cost-effective | Data quality issues if not monitored |
| Enables advanced analytics and AI | Requires skilled personnel to manage |
| Supports real-time processing | Security and compliance can be complex |
While the benefits are transformative, success depends on strong governance and clear strategies for managing vast, varied datasets.
Uses of Data Lake
The versatility of a Data Lake makes it a cornerstone of digital ecosystems. Its ability to handle unstructured data drives innovation across sectors.
Business Intelligence and Analytics
Organizations use Data Lakes to consolidate sales, marketing, and customer data. This leads to more accurate forecasting, efficient campaigns, and better customer experiences.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
Hospitals and research institutions analyze patient data, clinical trials, and medical images within Data Lakes to develop personalized treatments and predictive diagnostics.
IoT and Smart Systems
With billions of IoT devices generating data every second, Data Lakes collect and process it in real time—powering automation in cities, factories, and homes.
Financial Services
Banks and fintech firms rely on Data Lakes for fraud detection, risk assessment, and regulatory compliance through deep data analysis.
Research and Development
From tracking space missions to studying climate change, Data Lakes allow scientists to process massive data volumes that drive groundbreaking new inventions.
Resources
- AWS – Data Lakes on AWS
- Google Cloud – What is a Data Lake?
- Microsoft Azure – Introduction to Azure Data Lake.
- Databricks – Introduction to the well-architected data lakehouse
- IBM Cloud – Data Lake vs Data Warehouse Explained.
