In the world of cryptocurrency, securing your assets is paramount. One of the most reliable methods for doing so is by using a cold wallet. Unlike hot wallets, which stay connected to the internet, a cold wallet operates offline, making it less vulnerable to hacking attempts. Whether you’re new to cryptocurrency or an experienced trader, understanding the concept of a cold wallet can significantly impact how you protect your digital assets. This blog will explore what a cold wallet is, how it works, and its role in keeping your funds safe.
What is a Cold Wallet?
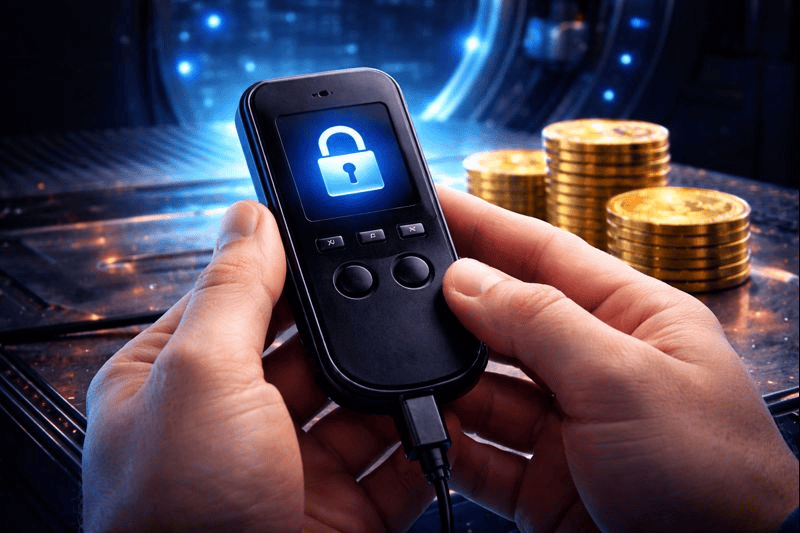

A cold wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that stores private keys offline, away from the internet. This makes it a safer option for long-term storage, as it greatly reduces the risk of cyberattacks and hacks. The cryptocurrency community also refers to cold wallets as “cold storage” or “hardware wallets.” Devices like Ledger and Trezor are popular examples of cold wallets and are frequently recommended for users who hold significant amounts of cryptocurrency, offering secure, offline storage for better protection against hacks and cyber threats.
Background
Cold wallets gained popularity as the cryptocurrency market expanded and cyber threats grew. Early on, people relied on software-based wallets connected to the internet. However, as hackers became more sophisticated, so did the need for more secure storage solutions. These wallets fill that need by being completely offline, with no active connection to the internet. Some users even go as far as storing their cold wallets in safety deposit boxes or other secure locations, ensuring maximum protection against both physical and online threats.
Key components of a cold wallet include a private key stored on a physical device and offline access. To transfer or access funds, users temporarily connect the cold wallet to an internet-enabled device. Once the transaction is complete, they disconnect the wallet, ensuring the private key stays offline and secure from potential online threats.
History
The concept of cold wallets became prominent in the early 2010s as cryptocurrency like Bitcoin started gaining mainstream attention. Early exchanges and investors quickly realized the vulnerability of keeping large amounts of digital assets online. The infamous Mt. Gox hack of 2014, where hackers stole millions worth of Bitcoin, further underscored the need for secure, offline storage solutions. Cold wallets emerged as a practical and secure alternative, particularly for long-term holders, or “HODLers,” of cryptocurrency.
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 2009 | Bitcoin launched, early online wallets used |
| 2013 | Hardware cold wallets like Trezor introduced |
| 2014 | Mt. Gox hack led to widespread cold wallet use |
Types of Cold Wallets
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices, often resembling USB drives (e.g., Ledger, Trezor), that securely store cryptocurrency offline.
- Paper Wallets: A printout of private and public keys, which can be stored physically. Although secure, this method is less user-friendly.
- Offline Software Wallets: Software installed on a computer or device that is never connected to the internet. Once transactions are signed, the wallet goes offline again.
| Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Wallet | Highly secure, easy to use | Can be expensive, physical loss risk |
| Paper Wallet | Free, highly secure when stored properly | Prone to damage or misplacement |
| Offline Software Wallet | Secure, no physical item to lose | Requires technical setup |
How Does a Cold Wallet Work?
A cold wallet works by storing the user’s private keys offline. To use a cold wallet, you generally need to connect it to a device temporarily to sign a transaction. The cold wallet generates a private key, which is never exposed to the internet, and signs transactions when necessary. This temporary connection ensures the private key stays offline, reducing exposure to malware or hacking attempts. Once the transaction is signed, the wallet disconnects, keeping the funds safe from online threats.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Protection from online threats and hacking | Less convenient for frequent transactions |
| Ideal for long-term storage | Can be expensive, especially hardware wallets |
| Multiple options for different needs | Losing the device or keys can result in lost funds |
Companies That Offer Cold Wallet Solutions
Ledger
Ledger is a leading provider of cold wallets, offering popular models like the Ledger Nano S and Nano X. Known for combining security and user-friendliness, these compact devices connect to computers or smartphones via USB or Bluetooth to sign transactions. Ledger emphasizes its Secure Element chip technology, which ensures private keys remain offline, adding extra protection. Trusted by individual investors and institutions alike, Ledger wallets are a top choice for secure cryptocurrency storage.
Trezor
Trezor, another prominent player in the cold wallet market, offers two main products: the Trezor Model One and Trezor Model T. SatoshiLabs launched Trezor, making it one of the first hardware wallets in the cryptocurrency space. It quickly gained trust within the community due to its transparency and robust security features. Trezor’s open-source nature allows users to verify its safety, which further strengthens its reputation as a reliable solution for securing digital assets. Trezor’s open-source firmware allows developers to review the code, ensuring there are no hidden vulnerabilities.
BitBox
The BitBox hardware wallet, created by the Swiss company Shift Cryptosecurity, is a more recent addition to the cold wallet market. Its BitBox02 model is known for its minimalist design and security-focused features. Unlike some competitors, BitBox emphasizes user privacy, requiring minimal personal information during setup. The device also supports backup and recovery using microSD cards, making it easy for users to secure their wallets. BitBox provides strong compatibility with Bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies and is lauded for its Swiss-level security standards. Its small form factor and ease of use have made it a favorite among users looking for a simple yet highly secure solution.
SafePal
SafePal is a rapidly growing hardware wallet provider, with backing from Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges in the world. The SafePal S1 hardware wallet offers a highly affordable option for users seeking cold storage without sacrificing security. Unlike other hardware wallets that require a USB or Bluetooth connection, the SafePal S1 operates using QR codes for transactions, which ensures the wallet remains fully air-gapped and never directly connects to the internet. SafePal supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies and is particularly favored by users in emerging markets due to its affordability. Its association with Binance adds an extra layer of credibility, especially for users familiar with the exchange’s platform.
Applications and Uses
Long-Term Investors
Cold wallets are ideal for long-term investors, often referred to as “HODLers” in the cryptocurrency community. These individuals purchase digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum and plan to hold onto them for years, expecting the value to appreciate over time. Since they don’t need regular access to their funds, it provide the highest level of security by keeping private keys offline. This reduces the risk of online hacking, phishing attacks, and malware. For long-term storage, devices like Ledger or Trezor are popular choices among investors to ensure their assets remain secure until they’re ready to sell.
Institutional Use and Cryptocurrency Exchanges

Cryptocurrency exchanges and large institutions also rely heavily on cold wallets to store a majority of their customers’ funds. Exchanges frequently face hacking attempts, so they store only a small portion of their funds in “hot wallets” for operational liquidity and keep the majority offline in cold wallets. This practice protects most assets, ensuring they remain safe even if the exchange gets compromised. For instance, Binance and Kraken use multi-signature cold wallets, requiring multiple parties to approve transactions before moving any funds, further enhancing their security.
High-Net-Worth Individuals or Traders
For high-net-worth individuals or traders who deal with large sums of cryptocurrency, cold wallets offer a robust solution for safeguarding assets. These users may not need frequent access to their funds but are more focused on keeping their investments safe from cybercriminals. Cold wallets offer peace of mind by ensuring that, even if hackers compromise internet-connected devices, the stored cryptocurrencies remain inaccessible and secure. Moreover, these individuals often back up their wallets with additional layers of security, such as biometric authentication or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Storing Rare or High-Value Digital Assets (NFTs and Tokens)
Cold wallets are increasingly used not only for cryptocurrencies but also for securing digital assets like Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). As the NFT market expands, so does the need to protect these valuable and unique digital collectibles from theft. Cold wallets store the private keys associated with NFTs, keeping high-value tokens secure offline. Digital artists and collectors often rely on hardware wallets to safeguard their NFTs, ensuring their collections remain safe and protected from online threats.
Companies Holding Cryptocurrencies as Part of Their Treasury
Many companies now hold cryptocurrencies as part of their financial treasury or investment portfolio. These companies use cold wallets to securely store significant amounts of Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other cryptocurrencies. By keeping their holdings in cold storage, they can protect their assets from online threats while still retaining the ability to access and move funds when needed. For example, companies like MicroStrategy and Tesla that hold large amounts of Bitcoin use cold storage solutions to keep their assets secure.
By applying cold wallets in these scenarios, users can confidently protect their cryptocurrency assets, whether they’re holding them for personal investments or large-scale corporate purposes.
Resources
- Tangem. What is a Cold Wallet?
- NFT Evening. How to Get a Crypto Wallet
- Investopedia. Cold Storage Definition
- Coinary. Understanding Cryptocurrency Cold Wallets
- Forbes. What is a Cold Wallet?
