In today’s fast-paced world of technology trends, software development is no longer just about writing great code — it’s about working together effectively. As projects grow larger and teams more distributed, collaboration, version control, and integration have become the heart of successful development. This is where platforms like Bitbucket make a significant impact.
Created to help teams collaborate on code efficiently, this Git-based hosting service goes far beyond being just a repository manager. It allows developers to share, review, and deploy code seamlessly across environments. Whether you’re a solo developer managing personal projects or part of a global engineering team, this platform ensures your workflow remains streamlined, consistent, and secure.
From integration with CI/CD pipelines to enhanced access control and project visibility, it represents how modern teams turn complex development processes into efficient, automated workflows.
What is Bitbucket?

At its core, Bitbucket is a Git-based source code management (SCM) platform designed to simplify team collaboration. It provides a space where developers can store, track, and manage their code, while also enabling peer reviews and streamlined deployment.
Developed by Atlassian, the same company behind Jira and Confluence, it connects project management and version control in one cohesive ecosystem. Teams can easily link their issue tracking with their repositories, creating a complete workflow — from planning to deployment — within a single platform.
Instead of dealing with fragmented tools, developers gain one centralized hub that supports both Git and Mercurial version control systems. With role-based access, integrated pull requests, and built-in CI/CD pipelines, it ensures both collaboration and security are part of the core development cycle.
This flexibility has made the platform especially popular with organizations embracing Agile and DevOps practices, where transparency, collaboration, and automation drive innovation.
Breaking Down Bitbucket
Bitbucket is built around several key features that make managing codebases efficient and scalable.
The foundation lies in repositories, which act as storage for project code and history. Each repository records every change made, making it easy for developers to track modifications, revert updates, and collaborate without overwriting each other’s work.
Next are branches, which allow multiple team members to work on different features simultaneously. Once the work is complete, these branches can be merged back into the main codebase through pull requests — a process that encourages team reviews and discussions before final integration.
Another critical feature is the pipeline automation tool, which enables continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). With this feature, every time code is pushed or merged, automated tests and deployments can be triggered, ensuring new features or fixes are stable and production-ready.
Additionally, integrations with Jira and Confluence create a complete project lifecycle solution. Developers can track progress, document updates, and link issues directly to code changes.
This combination of version control, automation, and collaboration makes it one of the most powerful development platforms in today’s ecosystem.
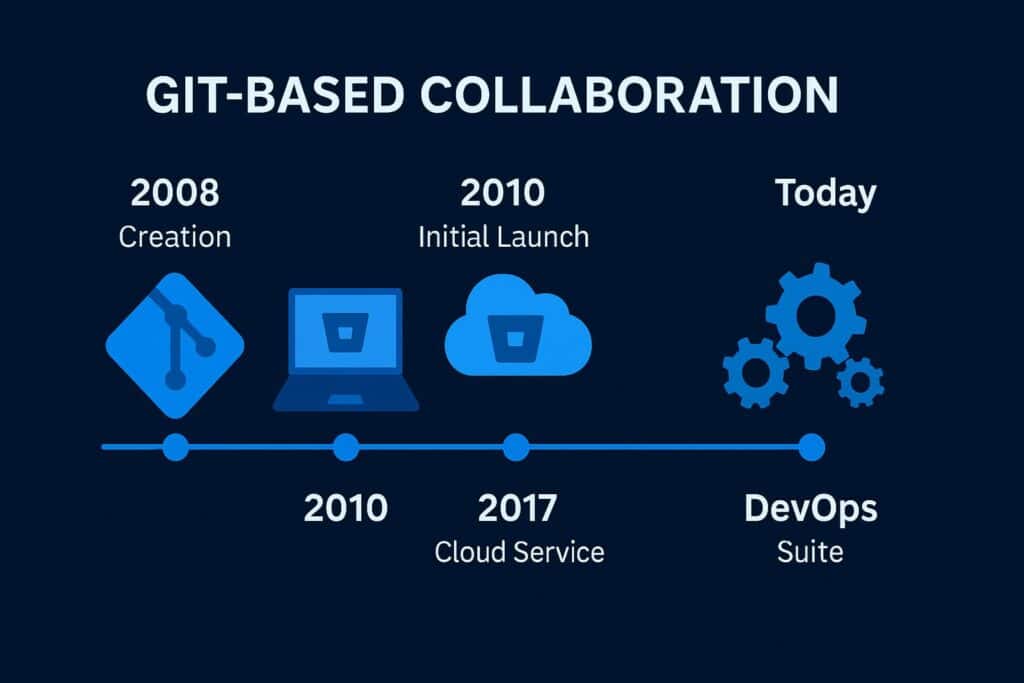
History of Bitbucket
The journey of Bitbucket began in 2008, when it was launched as a small project supporting the Mercurial version control system. As Git grew in popularity, the platform expanded its support in 2011, transforming into a robust, multi-system collaboration tool. Atlassian later acquired it, integrating it deeply into its suite of development and project management products.
Over the years, it evolved from a simple hosting service to an enterprise-grade collaboration environment. By incorporating DevOps features, enhanced permissions, and cloud-native scalability, it became an essential tool for modern software engineering teams.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | Initial Launch | Introduced as a Mercurial-based code hosting platform. |
| 2011 | Git Support Added | Expanded to support Git repositories. |
| 2012 | Acquired by Atlassian | Became part of the Atlassian product suite. |
| 2016 | Pipeline Integration | Introduced CI/CD pipelines for automation. |
| 2020–Present | Cloud-Native Focus | Enhanced scalability and enterprise-grade security features. |
From a niche repository manager to a global collaboration platform, it continues to empower developers and organizations to build faster and smarter through automation and integration.
Types of Bitbucket
Bitbucket comes in several variations designed to cater to different organizational needs and development styles.
Cloud Edition
The most widely used option, Bitbucket is fully hosted and managed by Atlassian. It provides seamless updates, automatic scaling, and integrations with tools like Jira, Trello, and Slack. Ideal for remote teams, it offers flexibility and minimal maintenance overhead.
Data Center Edition
This enterprise-focused deployment offers high availability, performance optimization, and advanced access controls. It’s preferred by large organizations that need control over infrastructure and security policies while maintaining the same features as the cloud version.
Server Edition
The self-hosted version (now in maintenance mode) allows teams to run the platform within their own environment. It was once popular among companies with strict data governance policies.
Integrated Tools and APIs
With a rich ecosystem of APIs and plugins, teams can extend functionality, connect CI/CD systems, or integrate with third-party applications like Jenkins or Bamboo.
Each edition gives organizations flexibility — from small startups needing simple cloud setups to enterprises managing thousands of repositories behind secure firewalls.
How Does Bitbucket Work?
This source code management platform operates by combining version control with collaboration and automation.
Developers begin by creating repositories where code is stored and versioned. Each change is tracked, allowing easy rollbacks and transparent progress. When a developer wants to add new features or fix bugs, they create branches. These branches isolate work so multiple people can contribute simultaneously without conflicts.
Once work is complete, a pull request initiates a peer review process. Other team members can comment, suggest changes, or approve the integration. After review, the branch is merged into the main codebase.
The system also includes built-in CI/CD pipelines that automate testing and deployment. Whenever new code is committed, the pipeline automatically runs checks to ensure everything works before pushing changes live.
This combination of automation and version control ensures that teams maintain code quality, accelerate delivery, and reduce manual overhead — a key advantage in Agile and DevOps-driven development.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Strong integration with Atlassian tools like Jira and Confluence | Limited free storage for large repositories |
| Built-in CI/CD pipelines for automation | May require learning curve for beginners |
| Secure collaboration and access control | Performance depends on network reliability |
| Scalable for teams of all sizes | Fewer integrations than some competitors |
| Supports both Git and Mercurial | Server edition is no longer actively developed |
Despite a few limitations, the platform remains a trusted solution for organizations seeking secure, collaborative, and automated version control.
Uses of Bitbucket
In Team Collaboration
This platform serves as a central hub for distributed teams, allowing them to contribute, review, and manage code together. With pull requests and inline commenting, it fosters open communication and accountability within projects.
In DevOps and Automation
Through integrated pipelines and API access, the platform supports automated testing, builds, and deployments. It’s a key component of continuous delivery workflows in Agile organizations.
In Project Management
When paired with Jira, developers can link tasks directly to code changes, providing full visibility into project progress and team productivity.
In Education and Open Source
Coding bootcamps and open-source projects use it to host shared repositories, helping students and contributors learn version control and collaboration best practices.
In Enterprise Development
Large organizations rely on the platform for managing thousands of repositories, maintaining version control, and ensuring compliance with security policies.
Its adaptability makes it a cornerstone in diverse environments — from small developer teams to global enterprises.
Resources
- Atlassian: Bitbucket Official Documentation
- Atlassian Blog: Integrating Jira with Bitbucket Pipelines
- TechTarget: Understanding Git Repository Management Tools
- IBM Developer: Continuous Integration Using Git Platforms
- DigitalOcean: Version Control for Teams
