In today’s fast-moving technology trends, speed, automation, and collaboration are the driving forces of success. Modern development teams need more than just tools — they need a connected ecosystem that manages projects, tests code, automates workflows, and delivers software continuously.
That’s where Azure DevOps enters the spotlight — a complete cloud-based development and delivery platform from Microsoft that unifies every stage of the software lifecycle. But it’s not just about writing or deploying code; it’s about creating synergy between people, processes, and automation.
In this article, we’ll explore what is Azure DevOps, its origins, how it works, its advantages, limitations, and how it continues to transform the way organizations build software around the world.
What is Azure DevOps?
At its core, this cloud-powered DevOps suite is designed to streamline software development and delivery. It integrates planning, coding, building, testing, and deployment into one seamless environment.
Instead of switching between multiple platforms, teams can manage repositories, track work items, automate pipelines, and monitor releases — all within a single interface. Think of it as a digital control tower that oversees every stage of the development journey.
This Microsoft-built development environment supports both cloud and on-premise infrastructures, making it flexible for small startups and large enterprises alike. It’s not just a tool — it’s a collaboration ecosystem built to unify developers, testers, and operations under one powerful umbrella.
Breaking Down Azure DevOps
This DevOps platform is composed of several interconnected services that function like building blocks of a complete software lifecycle. Each module focuses on a specific stage of development while staying connected to the others.
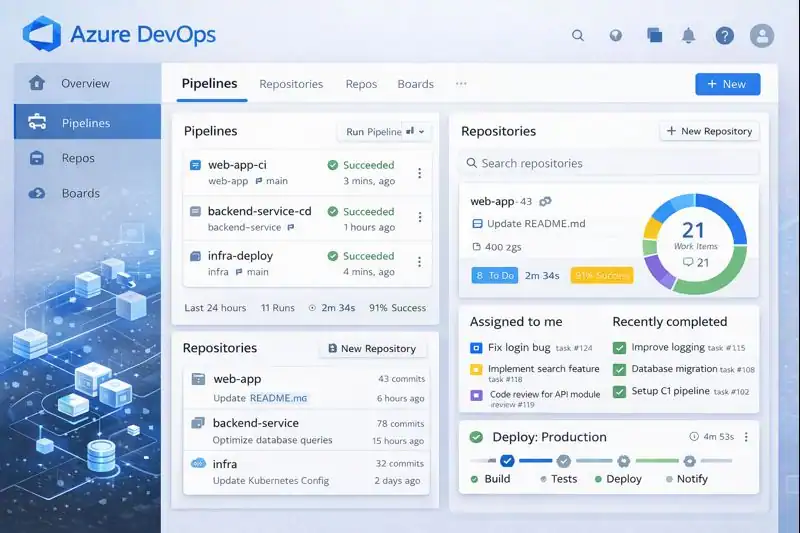
At the heart of the system lies Azure Repos, a Git-based source control system that manages and tracks code changes. Developers collaborate seamlessly, making commits, branches, and merges in real time.
Then there’s Azure Pipelines, the automation engine that powers continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD). It allows code to be built, tested, and deployed automatically — ensuring every change reaches users faster and more reliably.
Azure Boards manages project tasks and workflows, turning complex development cycles into visualized, trackable processes. Meanwhile, Azure Test Plans ensures quality through automated and manual testing frameworks.
Finally, Azure Artifacts acts as a secure library for managing dependencies and packages, helping teams maintain consistency across projects.
Each feature on its own is impressive — but together, they create an ecosystem that drives efficiency and innovation.
History of Azure DevOps
The journey of this Microsoft DevOps platform began in 2006 with Team Foundation Server (TFS) — a tool built to help teams manage version control and track work items. Over time, as cloud computing grew, Microsoft evolved TFS into Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS), introducing web-based collaboration and integration features.
In 2018, it underwent a complete transformation and rebranding to become Azure DevOps — representing Microsoft’s shift toward cloud-first, cross-platform development. The platform not only supports Microsoft technologies but also integrates seamlessly with open-source tools like GitHub, Jenkins, and Docker.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Launch of TFS | Version control and project management tool for enterprises. |
| 2012 | Visual Studio Online | Early move to cloud-based collaboration. |
| 2015 | Visual Studio Team Services | Full SaaS platform for DevOps pipelines. |
| 2018 | Azure DevOps Launch | Complete rebrand and expansion to multi-language, multi-cloud support. |
| 2020–Present | Continuous Growth | Ongoing innovation with GitHub Actions and hybrid DevOps integration. |
From on-prem servers to the cloud-native future, this development platform mirrors the evolution of how software itself is built and delivered.
Types of Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps Services (Cloud Version)
This hosted edition offers complete DevOps functionality on Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure. It’s ideal for teams that prefer scalability, automatic updates, and global accessibility without worrying about setup or maintenance.
Azure DevOps Server (On-Premise Version)
The self-managed version allows companies to host the system internally. It’s preferred by organizations with strict compliance or security requirements that want full control over data and environment configurations.
Hybrid Implementation
Some enterprises adopt a hybrid setup — combining the scalability of the cloud with the control of on-premises servers. This flexibility is especially valuable for regulated industries balancing security and agility.
Whether deployed in the cloud or locally, this collaboration suite provides the same consistent workflow, ensuring teams stay aligned regardless of infrastructure.
How Does Azure DevOps Work?

At its core, this CI/CD ecosystem automates every step of the development pipeline — from writing code to deploying updates in production.
When developers push code to Azure Repos, the Pipelines service automatically builds and tests it. If the build passes, it’s deployed to the desired environment, whether that’s a staging server, virtual machine, or container in the cloud.
Meanwhile, Boards track every feature, bug, or enhancement request, keeping everyone in sync. Teams can visualize progress using Kanban boards and sprint dashboards.
Test Plans validate application quality, running automated test suites to catch regressions early. Once a version is stable, Artifacts handle dependency management, ensuring every component is consistent across environments.
In essence, this DevOps framework turns chaos into coordination, creating a continuous feedback loop where teams can improve software faster and smarter.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Unified DevOps platform with strong integration | Can feel complex for small teams |
| Cloud scalability and accessibility | Pricing can increase with user growth |
| Excellent automation and CI/CD pipelines | Requires Microsoft account for access |
| Cross-platform and multi-language support | Learning curve for first-time users |
| Tight integration with GitHub and cloud tools | Customization may need advanced setup |
While it takes some time to master, the advantages — especially automation, collaboration, and flexibility — far outweigh the challenges.
Uses of Azure DevOps
In Software Development
This software delivery platform is used to automate builds, manage source control, and improve release frequency. Developers use it to ensure faster, more reliable code delivery.
In Continuous Integration and Delivery
Through Pipelines, it automates the entire CI/CD process. Teams can run tests, merge updates, and deploy apps with minimal manual input.
In Enterprise Project Management
Large companies use Boards to plan sprints, track progress, and maintain accountability across multiple teams and projects.
In Cloud Infrastructure Management
Integrations with Azure Cloud and Kubernetes make this automation framework ideal for deploying scalable applications directly to the cloud.
In Education and Training
Educational institutions use it to teach students about version control, DevOps principles, and cloud-native software practices in real-world environments.
From startups to global corporations, this Microsoft DevOps ecosystem continues to power productivity, innovation, and collaboration across industries.
Resources
- Microsoft Learn: Azure DevOps Documentation
- Atlassian Blog: Azure DevOps vs Jira Comparison
- TechTarget: What Is Azure DevOps?
- FreeCodeCamp: CI/CD for Beginners
- Docker Blog: Integrating Azure Pipelines with Docker
