Let’s go back in time a little. Do you recall those early science fiction films in which people had talking, decision-making, and occasionally even life-saving robot sidekicks? That’s no longer fiction, so welcome to the future. Our reality is summed up in a single buzzword: artificial intelligence agents.
You already interact with AI agents when you ask Siri to play your favorite playlist, use chatbots for customer service to resolve problems, or use intelligent systems to suggest your next program that you should binge-watch. The way we live, work, and make decisions is being altered by these digital brains. AI agents are the silent revolution creating noise in the background of the always changing tech trends, and they are only becoming more intelligent.
Let’s dissect everything in a way that is more akin to a coffee discussion than a textbook.
What is AI Agents?
Consider a digital assistant that can learn, adapt, and take action in addition to listening. Autonomous software programs created to sense their surroundings, make judgments, and act to accomplish predetermined objectives are what artificial intelligence (AI) agents are. They are the brains behind your favorite AI-powered features, if you will.
Although they go by a variety of names, including smart bots, digital agents, and intelligent agents, they are all primarily concerned with transforming data into action. They are the unsung heroes behind a lot of the smooth technology we use every day, from controlling emails to operating drones.
Breaking Down AI Agents
AI agents may seem complex at first, but let’s take a closer look.
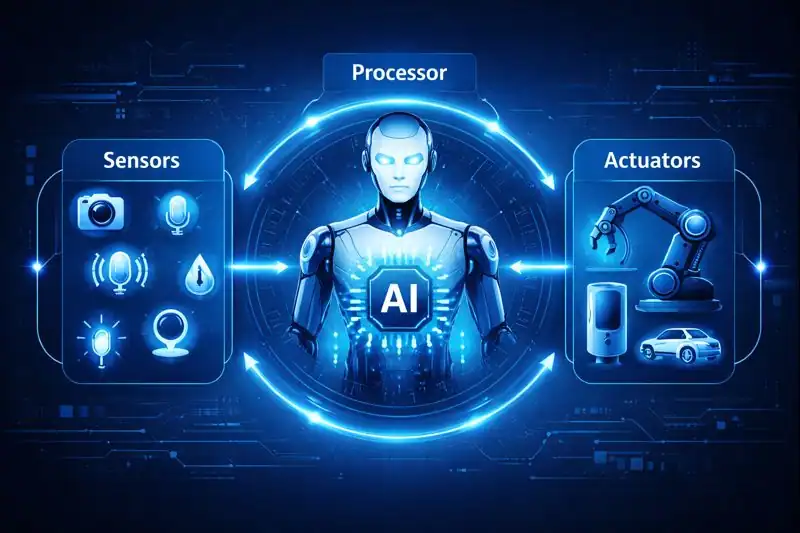
A number of essential elements make up an AI agent:
- Sensors: Sensors are the “eyes and ears” that gather data from the surroundings. They can be cameras, microphones, or software that retrieves information from the internet.
- Processor: The magic happens in this “brain.” It determines what to do after analyzing the information.
- Actuators: The “hands and feet” that perform the action, such as issuing an alert, moving a robot arm, or replying with text, are called actuators.
Here’s an example from real life. Consider utilizing a custom GPT, which is a modified form of a language model such as ChatGPT. You input the following task: “Set up a meeting with Sarah.”
History of AI Agents
The idea of AI agents is not particularly novel. The early aspirations for artificial intelligence in the 1950s marked the beginning of it all. At the time, scientists were fixated on building “thinking” machines.
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1956 | Birth of AI (Dartmouth Conference) | The dream of thinking machines began. |
| 1980s | Expert Systems | Early AI agents used to mimic decision-making in medicine and business. |
| 1990s | Rise of Intelligent Agents | Software that could learn and act started emerging in emails and data filtering. |
| 2010s | Smart Assistants | Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant entered our lives. |
| 2020s | Autonomous AI Agents | From self-driving cars to Salesforce Agentforce, AI agents now operate at scale. |
Over time, we’ve gone from rule-based systems to intelligent, adaptive models that feel almost…human.
Types of AI Agents

AI agents are not universally applicable. AI agents differ according to their complexity, functionality, and intended use, just as humans have diverse roles based on their personalities and skill sets. These digital workers fall into five major categories, each having a unique approach to decision-making and problem-solving.
Simple Reflex Agents
These are AI agents in their most basic form. They react immediately without taking the wider picture or prior experiences into account, operating just on the inputs that are currently available. Imagine the thermostat in your room; it detects the temperature and activates or deactivates the heating accordingly. There is only a direct response—neither memory nor prediction. Despite their simplicity, these agents perform exceptionally well in settings with known rules that don’t call for learning or adaptation.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based reflex agents are even more sophisticated and have some memory built in. They make better decisions by monitoring the internal status of the environment in addition to reacting to current input. For instance, consider a robotic vacuum cleaner. It does more than simply bump into furniture and turn; it creates a map of your area, identifies obstructions, and gradually refines its cleaning route. It can easily navigate more dynamic situations thanks to its memory-driven intelligence.
Goal-Based Agents
There is a purpose to these agents. Goal-based agents actively plan their activities to achieve a specified target rather than merely responding or adhering to preprogrammed behaviors. Consider how a GPS system, such as Google Maps, determines the optimal route for you based on your starting point, destination, and current traffic. When completing complicated activities that involve numerous steps and decisions along the way, these agents are extremely helpful.
Utility-Based Agents
Achieving a goal in the best manner is sometimes more important than just accomplishing it. Utility-based agents can help with that. These agents assess different results and choose the one that offers the most “utility,” or usefulness. AI agents, for example, constantly examine financial indicators and market trends when trading stocks in order to choose the best course of action. They optimize, striking a balance between risk, reward, and timing, rather than only acting.
Learning Agents
The closest thing to digital prodigies are the most sophisticated kind, known as learning agents. They do more than simply react, recall, or make plans; they gain knowledge from mistakes and get better with time. In order to improve their actions in response to criticism, achievements, or errors, these agents employ machine learning techniques. Netflix’s recommendation system is a prime example. It observes what you view, records what you enjoy (and don’t), and utilizes that information to recommend more relevant content. It eventually becomes frightfully adept at predicting your preferences before you do.
How Does AI Agents Work?
This is a detailed explanation of how these electronic brainiacs work:
- Perception: The agent receives information, such as a spoken command or a typed query.
- Interpretation: It recognizes the meaning of the input. Here, natural language processing, or NLP, is frequently involved.
- Decision-Making: The agent makes decisions based on its programming and objectives.
- Execution: It does something like reply to you, start a system, or communicate with another service.
- Learning (Optional): Depending on results or fresh information, certain agents gradually modify their behavior.
AI agents require context, objectives, and feedback in order to function effectively, much like a human assistant.
Pros & Cons
Let’s weigh the good and the not-so-good of using AI agents.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Automates repetitive tasks | Requires a lot of data |
| Enhances user experience | Can be expensive to develop |
| Operates 24/7 without fatigue | Risks of bias and errors |
| Learns and improves over time | Privacy and ethical concerns |
Uses of AI Agents
AI agents are now ubiquitous and not just found in tech labs.
Customer Service
Consider email responders, chatbots, and automated phone systems. AI agents are being utilized by businesses such as Salesforce Agentforce to efficiently manage thousands of support tickets.
Healthcare
AI agents are transforming healthcare, from handling patient records to identifying illnesses. They assist with scheduling, reminding people to take their medications, and even X-ray analysis.
Finance
AI agents are used by robo-advisors and fraud detection systems to make snap choices with little assistance from humans.
E-commerce
AI agents are used in chatbot help, dynamic pricing, and product recommendations. They facilitate and personalize online shopping.
Education
By providing resources according to performance and interest, AI tutors assist students with individualized learning paths.
Enterprise Applications
Consider data analytics tools, intelligent CRMs, and unique solutions like AI tools that are integrated with project management systems.
Resources
- IBM. What Are AI Agents and How They Work
- Google Cloud. What Are AI Agents
- Zapier. What Is an AI Agent?
- AWS. What Are AI Agents?
- BCG. How AI Agents Are Transforming Business
