The metaverse is rapidly transforming the digital economy, enabling users to interact, work, and do business in entirely new ways. With advancements in blockchain, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR), it offers vast potential for economic change across various sectors. From virtual real estate to digital goods and decentralized platforms, the metaverse presents both opportunities and challenges for businesses and individuals. Understanding its impact is essential as it reshapes global commerce, employment, and investment trends.
Overview of the Metaverse Economy
The metaverse is an interconnected digital space where users can engage in social interactions and business activities. It includes virtual worlds, digital assets, and decentralized platforms powered by technologies like blockchain and VR/AR. Unlike the traditional digital economy focused on e-commerce, the metaverse offers immersive experiences and true digital ownership through NFTs and cryptocurrencies. This enables activities like trading virtual land, collectibles, and services, creating a new economic frontier that goes beyond conventional boundaries.
Evolution of the Metaverse: Key Milestones
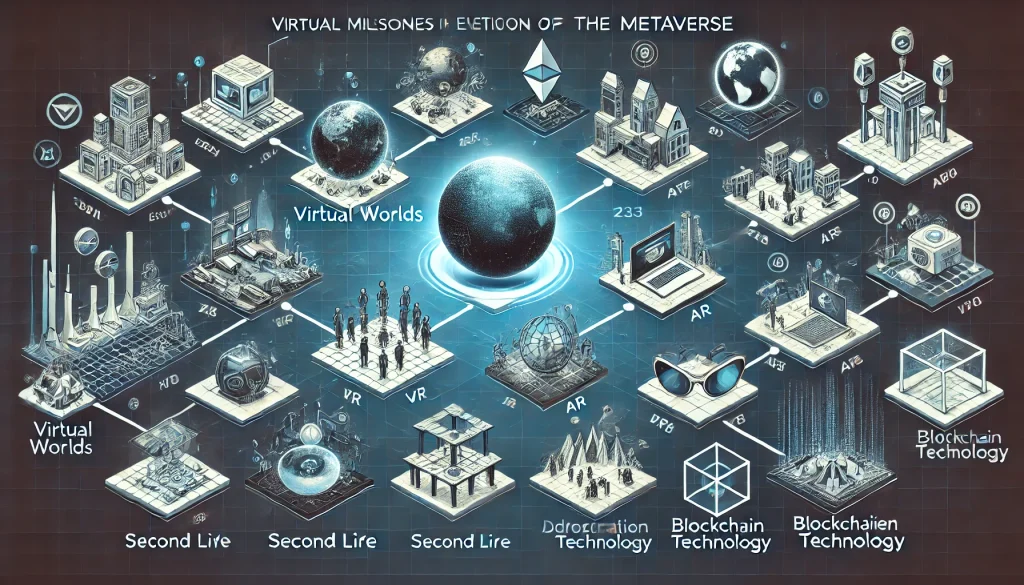
| Date | Event | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2003 | Launch of Second Life | Early exploration of virtual economies and digital commerce. |
| 2017 | Emergence of Decentraland | Introduction of blockchain-based ownership of virtual assets. |
| 2020 | Rise of NFTs | Monetization of digital art and collectibles. |
| 2024 | Integration of AR/VR in Metaverse Platforms | Enhanced user experiences and commercial applications. |
Key Components of the Metaverse Economy

Virtual Real Estate
Virtual real estate represents one of the most intriguing aspects of the metaverse economy. Users can buy, sell, and rent virtual land in platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox. Just like physical real estate, virtual properties can appreciate in value based on location, development, and demand. This has created a burgeoning market where investors and developers speculate on virtual land, driving up prices and creating new opportunities for digital entrepreneurs.
Digital Goods and Services
The metaverse has spawned a thriving market for digital goods and services. Users can purchase everything from virtual fashion and accessories for their avatars to digital art pieces that serve as NFTs. Brands are also establishing virtual stores to sell their products, offering unique shopping experiences and exclusive digital merchandise. This shift has opened up new revenue streams and creative possibilities for businesses and artists alike.
Virtual Employment
As the metaverse grows, so do job opportunities within these virtual worlds. People are finding work as content creators, virtual event managers, and even consultants for businesses looking to establish a presence in this virtual space. Virtual employment is not limited by geography, allowing a truly global workforce to participate in this new digital economy. This trend suggests that the online universe could become a significant source of income for millions in the future.
Cryptocurrencies and NFTs
Cryptocurrencies and NFTs form the backbone of the metaverse economy. They facilitate transactions and ownership of digital assets, making it possible to buy virtual land, trade digital art, and pay for services. Cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin are commonly used for transactions, while NFTs provide proof of ownership for unique digital items. Together, they enable a seamless and secure financial system within this virtual reality, fostering economic growth and innovation.
Economic Impact of the Metaverse
GDP Contribution
The metaverse could greatly boost global GDP, especially in gaming, entertainment, and virtual commerce. As investments in virtual assets and services grow, its economic impact may rival traditional digital economies. Analysts predict that by the end of the decade, the metaverse could contribute trillions of dollars to the global economy, fueled by increasing demand for digital experiences and assets.
Investment Trends
Investment in metaverse technologies and startups has skyrocketed recently, with venture capitalists, tech giants, and traditional financial institutions investing billions in virtual worlds, blockchain, and AR/VR tech. Corporations are also pursuing digital integrations, fueling a surge in mergers and acquisitions to capture a stake in this emerging market. This influx of capital is driving rapid innovation and expanding the metaverse’s potential applications.
Employment Opportunities
The online universe is creating new job categories and skill demands. From virtual architects who design digital spaces to blockchain developers and community managers, the opportunities are diverse and growing. Remote work within virtual environments offers flexibility and accessibility, enabling people from around the world to participate in the virtual world economy. As businesses increasingly operate in virtual spaces, the demand for skilled professionals in these new fields is likely to rise.
Regulatory Challenges
Despite its potential, the metaverse faces significant regulatory hurdles. Issues like data privacy, digital ownership rights, and taxation of virtual assets remain unresolved. Governments and regulatory bodies struggle to keep pace with the rapid development of this new digital economy, leading to uncertainty for businesses and users alike. Clear regulations are needed to protect participants while fostering innovation and growth within the online universe.
Sector-Specific Implications
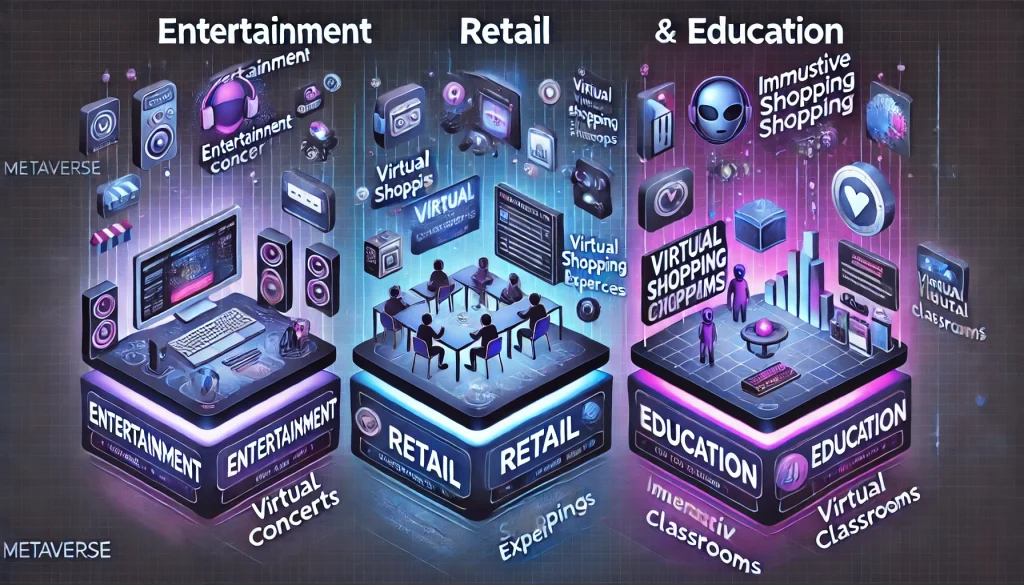
Entertainment and Media
The metaverse is revolutionizing the entertainment industry by offering immersive experiences such as virtual concerts, interactive digital art galleries, and virtual reality gaming. Artists and creators can reach global audiences without the constraints of physical venues, and fans can engage in new, interactive ways. This shift has the potential to redefine how we consume and participate in media and entertainment.
Retail and E-Commerce
Virtual stores are emerging as the next frontier for retail. Brands are setting up shop in virtual worlds, offering unique experiences that blend shopping with entertainment. Customers can explore digital showrooms, try on virtual outfits, and purchase both digital and physical goods. This integration of e-commerce into the metaverse provides businesses with innovative ways to connect with tech-savvy consumers.
Education and Training
The metaverse offers unprecedented opportunities for education and training. Virtual classrooms can provide immersive learning environments, allowing students to explore subjects like history or science in a fully interactive setting. Companies can also use virtual simulations for employee training, enabling more effective and engaging learning experiences. This approach has the potential to transform both traditional education and corporate training programs.
Comparing the Metaverse with Other Digital Economies
| Feature/Aspect | Metaverse Economy | Gig Economy | Traditional Internet Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Contribution | High potential, still emerging | Established but limited | High, mature |
| Regulatory Environment | Evolving, complex | Varied, dependent on location | Moderate, established |
| Employment Opportunities | New and emerging | Part-time, flexible | Diverse, remote and office-based |
Challenges and Opportunities in the Metaverse Economy
Challenges:
- Scalability Issues: Current technology struggles to support millions of simultaneous users in virtual spaces.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The metaverse is vulnerable to data breaches, hacking, and identity theft.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments lack clear regulations for virtual assets and transactions, creating legal ambiguities.
Opportunities:
- New Market Creation: The metaverse enables the development of entirely new markets for digital assets, services, and experiences.
- Innovative Business Models: Businesses can explore novel models like virtual real estate, NFT-based memberships, and digital goods.
- Global Collaboration: The metaverse offers a platform for international collaboration and innovation in a borderless digital environment.
Future Outlook for the Metaverse Economy
The metaverse economy’s future appears bright, fueled by advancements in VR/AR, 5G, and blockchain technology. These innovations will enhance user experiences and broaden the metaverse’s scope. Projected to grow exponentially over the next decade, the virtual world could revolutionize industries like gaming, entertainment, education, and finance. It will also impact social and cultural dynamics as virtual communities shape new ways of interacting, working, and socializing. Strategic investments and well-developed policies will be key to maximizing its economic potential while addressing emerging challenges.
Conclusion
The metaverse could reshape economic structures, offering new opportunities for businesses, individuals, and governments. Its impact spans sectors like entertainment, retail, and education, positioning it as a key player in the future digital economy. However, unlocking its full potential will require addressing regulatory and technological hurdles. As we enter this new digital era, strategic investments and proactive policies are crucial to building an inclusive metaverse economy.
FAQs
What is the metaverse and how does it differ from the traditional internet?
The metaverse is a virtual space where users can interact in immersive 3D environments. Unlike the traditional internet, it offers digital ownership through NFTs, real-time social interactions, and decentralized platforms, creating a more integrated and interactive experience.
How can businesses benefit from the metaverse economy?
Businesses can leverage the metaverse for virtual real estate, digital goods, and immersive marketing experiences. They can create virtual stores, host events, and engage with customers in new ways, opening up novel revenue streams and global reach.
What challenges does the metaverse face in terms of regulation?
The metaverse faces regulatory challenges such as unclear legal frameworks for digital ownership, data privacy, and taxation of virtual assets. Governments are still developing policies to address these issues, which could impact its growth and adoption.
Resources
- World Economic Forum. What Will Be the Economic Benefits of the Metaverse?
- Analysis Group. The Potential Global Economic Impact of the Metaverse
- McKinsey & Company. What Is the Metaverse?
- Techopedia. How Can the Metaverse Change the World?
- Forbes. The New Virtual Economy of the Metaverse
