In today’s data-driven age, Hadoop stands as one of the most revolutionary forces shaping technology trends. Every click, swipe, or voice command we make produces an ocean of data—and it helps make sense of it all. As a scalable and reliable framework, it empowers organizations to handle vast amounts of data with efficiency and speed. With this platform, businesses no longer drown in data—they thrive because of it. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, data scientist, or curious innovator, understanding this tool can redefine how you see the future of digital transformation.
What is Hadoop?
At its core, it is an open-source framework designed for distributed storage and processing of big data. In simple terms, it allows massive datasets to be stored and analyzed across clusters of computers. You can think of it as a digital engine powering data management systems in our modern world.
Unlike traditional databases that struggle with scalability, it thrives on expansion. It breaks down enormous data files into smaller chunks and processes them simultaneously. Thanks to this system, companies can handle exponential data growth without overwhelming their infrastructure.
Breaking Down Hadoop
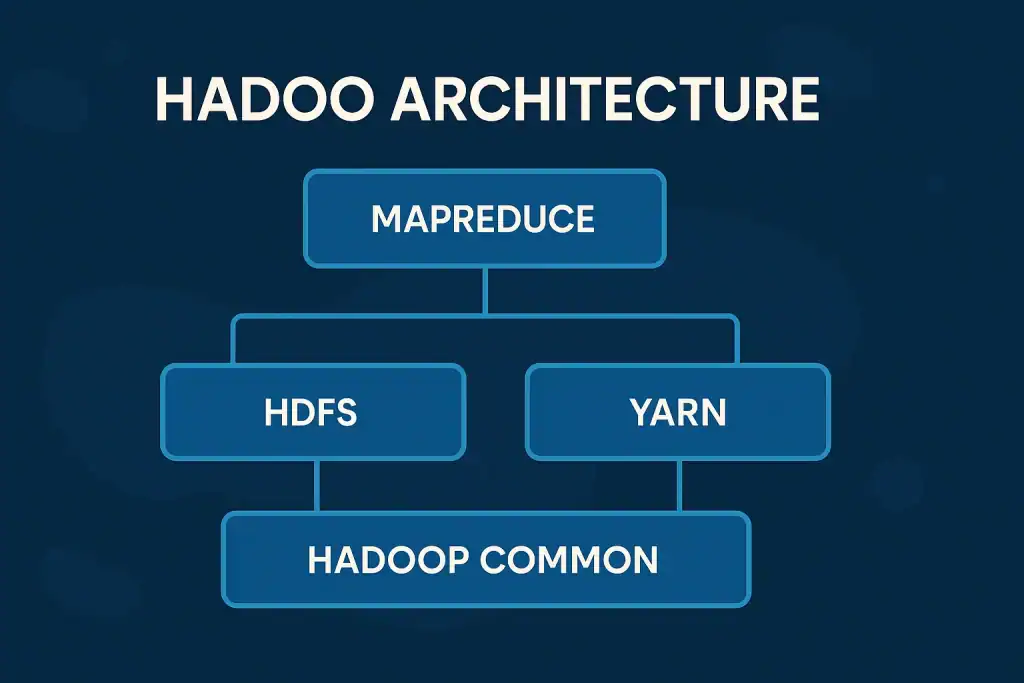
To truly appreciate this platform, we need to explore its components. The framework primarily consists of four key modules—Hadoop Common, Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), MapReduce, and YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator).
- Hadoop Common provides the necessary tools and libraries that other modules depend on.
- HDFS ensures that data is stored across multiple machines with redundancy for reliability.
- MapReduce handles the actual data processing, dividing tasks into smaller parts and executing them in parallel.
- YARN manages cluster resources efficiently, ensuring optimal use of computing power.
For instance, imagine analyzing customer data from millions of online transactions. Instead of one machine crunching the numbers for days, Hadoop divides the job among hundreds of computers, delivering results in minutes. It’s like having a symphony of machines playing in perfect harmony.
History of Hadoop
The journey of this software began in the early 2000s. Inspired by Google’s revolutionary papers on distributed systems, Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella created Hadoop to power their open-source search engine project called Nutch. Over time, it evolved from a humble experiment to a global phenomenon in big data management.
| Year | Milestone | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Nutch Project | Initial idea for scalable web crawling and indexing |
| 2005 | Hadoop Birth | Officially separated from Nutch for data processing |
| 2008 | Apache Adoption | Became an Apache Software Foundation project |
| 2011 | Commercial Adoption | Enterprises began integrating Hadoop for analytics |
| 2020s | Modern Integration | Enhanced to work with cloud and real-time data tools |
This historical evolution showcases how an innovation from a small open-source effort became a cornerstone of advanced technology.
Types of Hadoop

1. Hadoop 1.0 (Classic Version)
The first generation introduced MapReduce and HDFS, enabling distributed storage and computation. It laid the groundwork for what would become a data revolution.
2. Hadoop 2.0 (Enhanced Version)
This version brought YARN, allowing multiple applications to run simultaneously on a single cluster. It improved flexibility, scalability, and efficiency.
3. Hadoop 3.0 and Beyond
Modern Hadoop integrates seamlessly with cloud platforms and supports containerization technologies like Docker. This version is built for futuristic technology, enabling real-time data analytics and AI-driven insights.
How Does Hadoop Work?
Let’s visualize how this open-source platform functions. When data enters the system, it’s divided into smaller blocks. These blocks are stored across various nodes within the HDFS. The MapReduce engine then processes these data blocks in parallel, assigning tasks to nodes closest to where the data resides—this reduces network congestion and boosts performance.
Next, YARN takes control by managing resources and scheduling jobs efficiently. Once all computations are complete, results are merged and delivered as unified output.
For example, a retail company using the software might analyze customer behavior data from IoT devices across the globe. Instead of one central server, thousands of machines work together to extract insights—revealing patterns, predicting trends, and optimizing marketing strategies.
This process highlights Hadoop’s brilliance: simple, scalable, and swift.
Pros & Cons
While this data framework offers remarkable advantages, it’s not without challenges.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Scalable to handle petabytes of data | Requires skilled professionals |
| Cost-effective open-source framework | Not ideal for small datasets |
| Fault-tolerant architecture | Complex setup and maintenance |
| Integrates well with cloud systems | High learning curve for beginners |
| Supports real-time analytics | Security configuration can be demanding |
Beyond the table, it’s essential to understand how these points play out in real-world settings. Large enterprises benefit immensely from its scalability, especially when dealing with massive volumes of unstructured information. Its distributed system ensures that even if one server fails, operations continue smoothly—something traditional storage systems struggle to achieve.
However, there’s no denying the steep learning curve. Implementing and maintaining such a vast ecosystem demands technical expertise and careful planning. Smaller organizations may find setup costs or maintenance overheads challenging. Still, for those aiming to harness the full power of big data processing, this open-source ecosystem remains one of the most reliable, resilient, and forward-thinking technologies driving digital transformation today.
Uses of Hadoop
Big Data Analytics
Enterprises leverage the use of this platform for processing huge data volumes to uncover actionable insights. Financial institutions use it to detect fraud, while retailers use it to analyze buying habits.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
With the rise of iot devices, it plays a vital role in processing continuous data streams from smart devices. It allows companies to monitor operations, optimize systems, and predict equipment failures.
Research and Science
In scientific fields, it helps analyze complex datasets—like genomic sequences or environmental data—faster than ever before. Researchers can now explore patterns that were once impossible to see.
Social Media and Marketing
Platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn utilize it for user behavior analysis and ad targeting. With real-time insights, marketers can personalize campaigns to boost engagement and sales.
In each scenario, it stands as the backbone of new inventions and advanced technology, turning raw information into meaningful intelligence.
Resources
Apache Hadoop – Official Documentation
IBM – Understanding Hadoop and Big Data
Coursera – What Is Hadoop?
Databricks – What Is Hadoop?
TechTarget – Hadoop Explained
