The first time I installed an SSD in my laptop, it felt like I had given my aging machine a second life. My old hard drive had been sluggish—booting up took minutes, and opening large files felt like waiting for a snail to cross the road. But the moment I switched to solid-state storage, everything changed. My computer powered up in seconds, programs launched instantly, and I couldn’t stop smiling. That’s when I truly began to wonder, and why does it make such a remarkable difference?
We celebrate powerful processors and flashy graphics cards, but without efficient storage, our digital lives would crawl. It has quietly become one of the most transformative technologies of the last decade. From personal laptops to enterprise servers, it’s redefining performance and reliability.
What is an SSD?
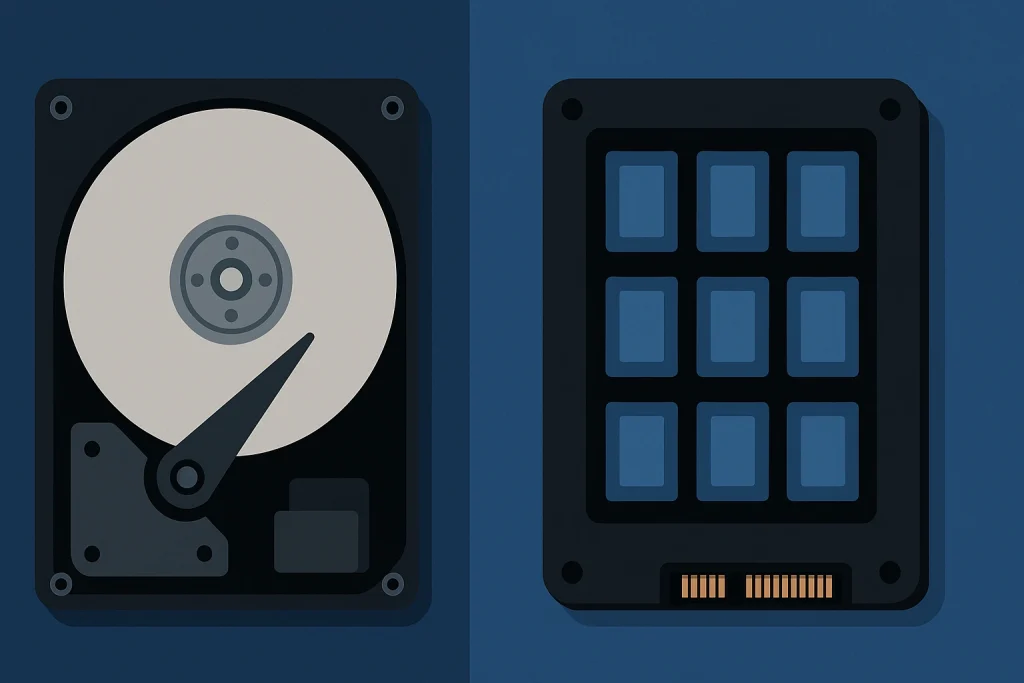

SSD stands for Solid-State Drive, a type of storage device that uses flash memory instead of spinning magnetic disks. Unlike traditional hard drives (HDDs), it has no moving parts. This single difference makes it dramatically faster, more reliable, and far less prone to failure from drops or shocks.
So, the answer is simple: it’s a storage device designed for speed, durability, and efficiency. While HDDs are like vinyl records, reading data with a physical needle, they are more like giant USB flash drives—quick, silent, and modern. They allow your computer to boot in seconds, cut game loading screens to almost nothing, and make file transfers feel instantaneous.
Because there are no moving parts, they also generate less heat and consume less power, which is especially important for laptops and mobile devices. In short, it represents the natural evolution of storage technology, combining performance with resilience in a way older drives simply can’t match.
Breaking Down SSDs
At first glance, it might just look like a sleek black rectangle, but inside, it’s a marvel of engineering simply a real game changer. The key components include:
NAND Flash Memory
This is the heart of the drive, the actual place where your data lives. NAND flash is made up of memory cells that store information as electrical charges. Unlike traditional hard drives with spinning disks, NAND has no moving parts, which makes SSDs faster, quieter, and more durable. The type of NAND (such as SLC, MLC, TLC, or QLC) also influences performance and lifespan—SLC is the fastest and most durable, while QLC is cheaper but slightly slower.
Controller
The controller acts as the SSD’s brain—a dedicated microprocessor that determines where data is stored, how it’s retrieved, and how to balance wear across the memory cells. It also handles advanced functions like error correction, encryption, and garbage collection. A strong controller can make the difference between a budget SSD and a high-end drive that runs reliably for years.
Cache
Think of cache as the SSD’s quick-access notepad. It’s temporary storage that holds frequently used data or files in transition, allowing the system to pull them up almost instantly. Many SSDs use DRAM or SLC cache to smooth performance during large file transfers. Without this buffer, even a fast drive could slow down under heavy workloads.
History of SSDs
The journey began long before they entered consumer laptop. In fact, early versions appeared in the 1950s, though they were bulky and impractical. It wasn’t until flash memory was developed in the late 1980s it became viable for widespread use.
By the mid-2000s, it began appearing in high-end laptops and enterprise systems. Though expensive at first, prices have steadily dropped, making them mainstream. The introduction of NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) in the 2010s revolutionized speed even further, allows it to reach lightning-fast transfer rates.
| Decade | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1950s | Early experimental solid-state storage |
| 1980s | Flash memory invented |
| 1990s | used in military and industrial systems |
| 2000s | Consumer laptops begin adopting |
| 2010s | NVMe revolutionize performance |
| 2020s | Dominate both personal and enterprise storage markets |
Types of SSDs
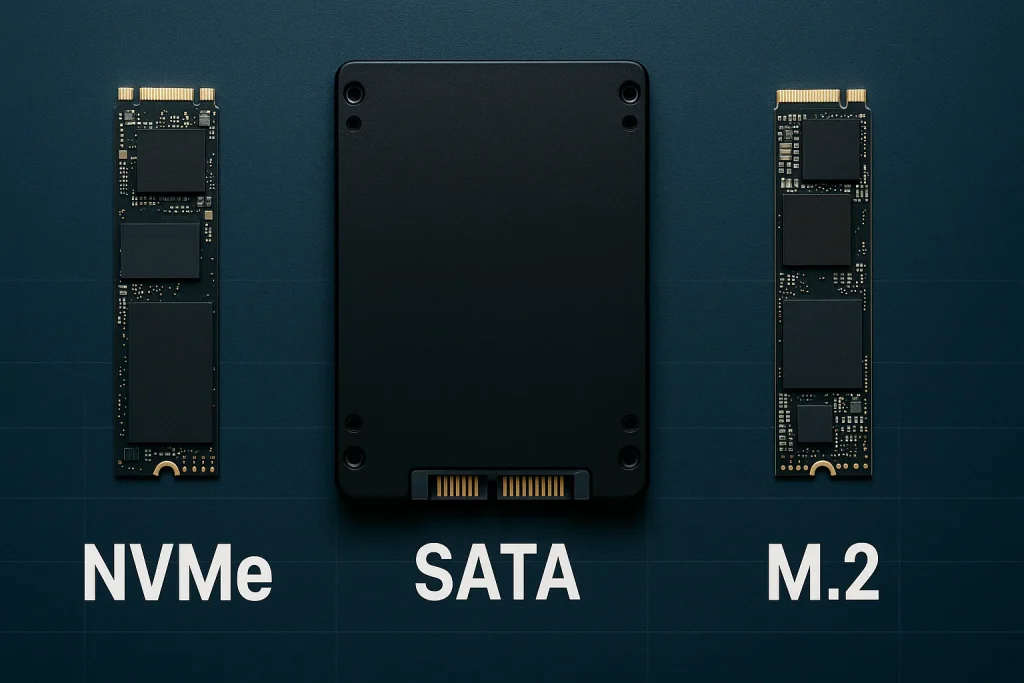
SATA SSD
The most common type, SATA connect using the same interface as older hard drives. They’re much faster than HDDs but limited by SATA speeds. Perfect for upgrading older machines.
NVMe SSD
Connected via PCIe, these drives are significantly faster, capable of handling heavy workloads like 4K video editing and gaming. If SATA are like sports cars, NVMe drives are jet planes.
M.2 SSD
A compact form factor that slides directly into a slot on the motherboard. M.2 can be either SATA or NVMe, and they’re popular for ultrabooks and slim laptops.
External SSD
Portable drives that connect via USB or Thunderbolt. They’re ideal for photographers, videographers, or anyone needing fast storage on the go.
How Do SSDs Work?
Understanding also means exploring how it functions. Unlike HDDs, which rely on spinning disks, it also uses interconnected flash memory chips to store data. Here’s the process:
When you save a file, the controller breaks it into blocks.
These blocks are stored in NAND flash cells.
When you access the file, the controller instantly retrieves the blocks.
With no mechanical movement involved, the process is nearly instantaneous.
Think of it like this: finding data on an HDD is like waiting for a record player needle to find the right groove, while accessing data on it is like tapping a playlist on your phone—fast, responsive, and effortless every single time.
Pros & Cons
Powerful, but like any technology, they come with both strengths and limitations.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Blazing-fast speed | Higher cost per gigabyte |
| No moving parts | Limited write cycles |
| Energy-efficient | Performance varies by type |
| Silent operation | Smaller capacities compared to HDDs |
Uses of SSDs
The uses are vast, cutting across major industries and helping a lot of personal needs alike.
Everyday Computing
For the average user, it makes laptops and desktops boot up in milliseconds and apps load instantly without the frustration of delay. Once you’ve experienced it, going back to HDDs feels painful.
Gaming
Gamers benefit hugely. Faster load times mean less waiting between levels and more time immersed in the action. Many modern consoles now ship with it by default.
Creative Work
Photographers, filmmakers, and designers rely on them to handle massive files. Editing high-resolution video or working with layered images becomes seamless with fast storage.
Enterprise & Cloud
Servers and cloud services depend for quick data access and reliability. Imagine an e-commerce site handling thousands of orders per minute keep everything running without delays.
Resources
- Samsung: What is an SSD?
- Crucial: How Do SSDs Work?
- Kingston: SSD vs HDD: What’s the Difference?
- Intel: Understanding NVMe SSDs
- TechRadar: Best SSDs for 2025
